Promising algorithms to perilous applications: a systematic review of risk stratification tools for predicting healthcare utilisation
- PMID: 38901863
- PMCID: PMC11191805
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjhci-2024-101065
Promising algorithms to perilous applications: a systematic review of risk stratification tools for predicting healthcare utilisation
Abstract
Objectives: Risk stratification tools that predict healthcare utilisation are extensively integrated into primary care systems worldwide, forming a key component of anticipatory care pathways, where high-risk individuals are targeted by preventative interventions. Existing work broadly focuses on comparing model performance in retrospective cohorts with little attention paid to efficacy in reducing morbidity when deployed in different global contexts. We review the evidence supporting the use of such tools in real-world settings, from retrospective dataset performance to pathway evaluation.
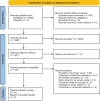
Methods: A systematic search was undertaken to identify studies reporting the development, validation and deployment of models that predict healthcare utilisation in unselected primary care cohorts, comparable to their current real-world application.
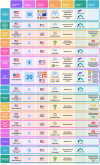
Results: Among 3897 articles screened, 51 studies were identified evaluating 28 risk prediction models. Half underwent external validation yet only two were validated internationally. No association between validation context and model discrimination was observed. The majority of real-world evaluation studies reported no change, or indeed significant increases, in healthcare utilisation within targeted groups, with only one-third of reports demonstrating some benefit.
Discussion: While model discrimination appears satisfactorily robust to application context there is little evidence to suggest that accurate identification of high-risk individuals can be reliably translated to improvements in service delivery or morbidity.
Conclusions: The evidence does not support further integration of care pathways with costly population-level interventions based on risk prediction in unselected primary care cohorts. There is an urgent need to independently appraise the safety, efficacy and cost-effectiveness of risk prediction systems that are already widely deployed within primary care.
Keywords: Decision Support Systems, Clinical; Electronic Health Records; Primary Health Care; Public Health; Safety Management.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HA is the chief scientific officer of Preemptive Health and Medicine and Flagship Pioneering. JM was paid directly for giving a lecture at Health Education England on the topic of artificial intelligence in the NHS. JM has been a member of the INSIGHT DataTAB for HDR UK. JZ is employed as a Senior Informatician by Arcturis Data, a Real-World Data company.
Figures

References
-
- NHS England . Risk stratification. 2023. Available: https://www.england.nhs.uk/ig/risk-stratification/ [Accessed 28 Nov 2023].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
