Bifocal diffractive lenses based on the aperiodic Kolakoski sequence
- PMID: 38902352
- PMCID: PMC11189935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-64800-3
Bifocal diffractive lenses based on the aperiodic Kolakoski sequence
Abstract
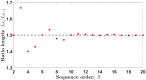
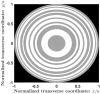
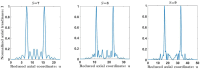
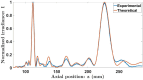
In this work, we present a new family of Zone Plates (ZPs) designed using the self-generating Kolakoski sequence. The focusing and imaging properties of these aperiodic diffractive lenses coined Kolakoski Zone Plates (KZPs) are extensively studied. It is shown that under monochromatic plane-wave illumination, a KZP produces two main foci of the same intensity along the axial axis. Moreover, one of the corresponding focal lengths is double the other, property correlated with the involved aperiodic sequence. This distinctive optical characteristic is experimentally confirmed. We have also obtained the first images provided by these bifocal new diffractive lenses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Wang S, Zhang XC. Terahertz wave tomographic imaging with a Fresnel lens. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2003;1:53–55.
-
- Ojeda-Castaneda J, Gomez-Reino CC, editors. Selected Papers on Zone Plates. Washington: SPIE Optical Engineering Press; 1996.
-
- Soret J. Ueber die durch kreisgitter erzeugten diffractionsphnomene. Annalen der Physik und Chemie. 1875;232:99–113. doi: 10.1002/andp.18752320906. - DOI
-
- Geints YE, Panina EK, Minin IV, Minin OV. Study of focusing parameters of wavelength-scale binary phase Fresnel zone plate. J. Opt. 2021;23:065101. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/abf891. - DOI
Grants and funding
- PID2022-142407NB-100/Ministerio de Ciencias e Innovación, Spain
- PID2022-142407NB-100/Ministerio de Ciencias e Innovación, Spain
- PID2022-142407NB-100/Ministerio de Ciencias e Innovación, Spain
- PID2022-142407NB-100/Ministerio de Ciencias e Innovación, Spain
- PID2022-142407NB-100/Ministerio de Ciencias e Innovación, Spain

