First-in-human, double-blind, randomized phase 1b study of peptide immunotherapy IMCY-0098 in new-onset type 1 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of immune biomarkers
- PMID: 38902652
- PMCID: PMC11191262
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03476-y
First-in-human, double-blind, randomized phase 1b study of peptide immunotherapy IMCY-0098 in new-onset type 1 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of immune biomarkers
Abstract
Background: IMCY-0098, a synthetic peptide developed to halt disease progression via elimination of key immune cells in the autoimmune cascade, has shown a promising safety profile for the treatment of type 1 diabetes (T1D) in a recent phase 1b trial. This exploratory analysis of data from that trial aimed to identify the patient biomarkers at baseline associated with a positive response to treatment and examined the associations between immune response parameters and clinical efficacy endpoints (as surrogates for mechanism of action endpoints) using an artificial intelligence-based approach of unsupervised explainable machine learning.
Methods: We conducted an exploratory analysis of data from a phase 1b, dose-escalation, randomized, placebo-controlled study of IMCY-0098 in patients with recent-onset T1D. Here, a panel of markers of T cell activation, memory T cells, and effector T cell response were analyzed via descriptive statistics. Artificial intelligence-based analyses of associations between all variables, including immune responses and clinical responses, were performed using the Knowledge Extraction and Management (KEM®) v 3.6.2 analytical platform.
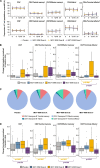
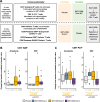
Results: The relationship between all available patient data was investigated using unsupervised machine learning implemented in the KEM® environment. Of 15 associations found for the dose C group (450 μg subcutaneously followed by 3 × 225 μg subcutaneously), seven involved human leukocyte antigen (HLA) type, all of which identified improvement/absence of worsening of disease parameters in DR4+ patients and worsening/absence of improvement in DR4- patients. This association with DR4+ and non-DR3 was confirmed using the endpoints normalized area under the curve C-peptide from mixed meal tolerance tests where presence of DR4 HLA haplotype was associated with an improvement in both endpoints. Exploratory immune analysis showed that IMCY-0098 dose B (150 μg subcutaneously followed by 3 × 75 μg subcutaneously) and dose C led to an increase in presumed/potentially protective antigen-specific cytolytic CD4+ T cells and a decrease in pathogenic CD8+ T cells, consistent with the expected mechanism of action of IMCY-0098. The analysis identified significant associations between immune and clinical responses to IMCY-0098.
Conclusions: Promising preliminary efficacy results support the design of a phase 2 study of IMCY-0098 in patients with recent-onset T1D.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03272269; EudraCT: 2016-003514-27.
Keywords: Beta cells; Exploratory analysis; Immune biomarker machine learning; Immunotherapy; T cells; Type 1 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JVR, VC, NB, LV, MVM, and PV are employees or contractors of Imcyse S.A., Liège, Belgium, and may hold stock options. MK and FP are employees of Ariana Pharmaceuticals SA. RDL’s institution received study funding and materials from Imcyse. RDL received honorarium from DMRR and took part in advisory boards for Diamyd and Provention. CB’s institutions received study funding and materials from Imcyse. PA declares no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Global report on diabetes. World Health Organization: World Health Organization; 2016. Available from: https://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/.
-
- Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Supplement 1):S13–S22. - PubMed
-
- Nowak C, Hannelius U, Ludvigsson J. Association between treatment effect on C-peptide preservation and HbA1c in meta-analysis of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)-alum immunotherapy in recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, obes metab. 2022;24(8):1647–1655. doi: 10.1111/dom.14720. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- LeFevre JD, Cyriac SL, Tokmic A, Pitlick JM. Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies for the prevention and treatment of type 1 diabetes: a literature review. AJHP. 2022. 10.1093/ajhp/zxac244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

