Repeated COVID-19 Vaccination Drives Memory T- and B-cell Responses in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Results From a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38902860
- PMCID: PMC11581438
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000005119
Repeated COVID-19 Vaccination Drives Memory T- and B-cell Responses in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Results From a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Insight into cellular immune responses to COVID-19 vaccinations is crucial for optimizing booster programs in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs).
Methods: In an immunologic substudy of a multicenter randomized controlled trial (NCT05030974) investigating different repeated vaccination strategies in KTR who showed poor serological responses after 2 or 3 doses of an messenger RNA (mRNA)-based vaccine, we compared SARS-CoV-2-specific interleukin-21 memory T-cell and B-cell responses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISpot) assays and serum IgG antibody levels. Patients were randomized to receive: a single dose of mRNA-1273 (100 μg, n = 25), a double dose of mRNA-1273 (2 × 100 μg, n = 25), or a single dose of adenovirus type 26 encoding the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (Ad26.COV2.S) (n = 25). In parallel, we also examined responses in 50 KTR receiving 100 μg mRNA-1273, randomized to continue (n = 25) or discontinue (n = 25) mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid. As a reference, the data were compared with KTR who received 2 primary mRNA-1273 vaccinations.
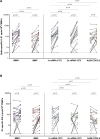
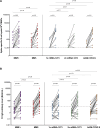
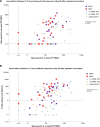
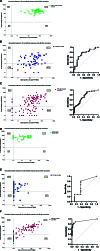
Results: Repeated vaccination increased the seroconversion rate from 21% to 66% in all patients, which was strongly associated with enhanced levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific interleukin-21 memory T cells (odd ratio, 3.84 [1.89-7.78]; P < 0.001) and B cells (odd ratio, 35.93 [6.94-186.04]; P < 0.001). There were no significant differences observed in these responses among various vaccination strategies. In contrast to KTR vaccinated with 2 primary vaccinations, the number of antigen-specific memory B cells demonstrated potential for classifying seroconversion after repeated vaccination (area under the curve, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.90; P = 0.26 and area under the curve, 0.95; confidence interval, 0.87-0.97; P < 0.0001, respectively).
Conclusions: Our study emphasizes the importance of virus-specific memory T- and B-cell responses for comprehensive understanding of COVID-19 vaccine efficacy among KTR.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sanders J-SF, Bemelman FJ, Messchendorp AL, et al. ; RECOVAC Collaborators. The RECOVAC Immune-response Study: the immunogenicity, tolerability, and safety of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with chronic kidney disease, on dialysis, or living with a kidney transplant. Transplantation. 2022;106:821–834. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reddy S, Chitturi C, Yee J. Vaccination in chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019;26:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Heeger PS, Larsen CP, Segev DL. Implications of defective immune responses in SARS-CoV-2 vaccinated organ transplant recipients. Sci Immunol. 2021;6:eabj6513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

