Research progress of megakaryocytes and platelets in lung injury
- PMID: 38902986
- PMCID: PMC11195464
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2362871
Research progress of megakaryocytes and platelets in lung injury
Abstract
The lung is an important site of extramedullary platelet formation, and megakaryocytes in the lung participate in immune responses in addition to platelet production. In acute lung injury and chronic lung injury, megakaryocytes and platelets play a promoting or protective role through different mechanisms. The authors reviewed the role of megakaryocytes and platelets in common clinical lung injuries with different course of disease and different pathogenic factors in order to provide new thinking for the diagnosis and treatment of lung injuries.
Keywords: Megakaryocytes; acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; chronic lung injury; platelets.
Plain language summary
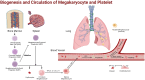
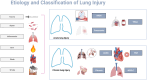
What is the context?Platelets are specialized non-nucleated blood cells produced by cytoplasmic lysis of megakaryocytes.HSCs differentiate into granular mature megakaryocytes and produce platelets.Lung is a reservoir of megakaryocytes and a site where platelets are produced in addition to bone marrow and spleen.Lung injury can be divided into acute lung injury and chronic lung injury, and characterized by different pathogenesis.Platelets and megakaryocytes are involved in hemostasis and regulation of the body ‘s inflammatory response.The disease state of the lung affects the functions of megakaryocytes and platelets.The role of megakaryocytes and platelets in acute and chronic lung injury is poorly studied.What is new?Platelets in the lung are derived not only from the spleen and bone marrow, but also from megakaryocytes in the pulmonary circulation. In this study, we demonstrated that pulmonary megakaryocytes not only produce platelets to play a hemostatic role in lung injury, but also participate in inflammation and immune response with platelets to promote the process of lung injury or play a protective role.Therefore, it was suggested in our analysis that targeting lung megakaryocytes and platelets is currently a new direction for the treatment of a variety of lung injuries.What is the impact?This review intends to explain the relationship between megakaryocytes, platelets and many types of lung injury from the mechanism of platelet production in the lung, and make a prospect in the new progress in the diagnosis and treatment of lung injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
