The cepacian-like exopolysaccharide of Paraburkholderia ultramafica STM10279T enhances growth and metal adaptation of Tetraria comosa on New Caledonian ultramafic soil
- PMID: 38903440
- PMCID: PMC11188366
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1349724
The cepacian-like exopolysaccharide of Paraburkholderia ultramafica STM10279T enhances growth and metal adaptation of Tetraria comosa on New Caledonian ultramafic soil
Abstract
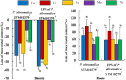
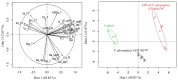
Paraburkholderia ultramafica STM10279T is a metal-tolerant rhizobacterium that promotes plant growth. It was isolated from the roots of Tetraria arundinaceae, a pioneer endemic tropical herb growing on ultramafic soils in New Caledonia. We have recently shown that the main mechanism of metal tolerance of P. ultramafica is related to the production of an acidic exopolysaccharide (EPS). To explore the potential role of this EPS in the plant's environmental adaptation, we first elucidated its structure by employing a combination of chromatography and mass spectrometry techniques. These analyses revealed that the EPS is highly branched and composed of galactosyl (35.8%), glucosyl (33.2%), rhamnosyl (19.5%), mannosyl (7.2%), and glucuronosyl residues (4.4%), similar to the EPS of the Burkholderia cepacia complex known as cepacian. We subsequently conducted greenhouse experiments on Tetraria comosa plantlets inoculated with P. ultramafica or a solution of its EPS during transplanting onto ultramafic substrate. The data showed that the dry weight of T. comosa shoots was 2.5 times higher in the plants treated with the EPS compared to the unexposed plants. In addition, inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis revealed that exposure to the EPS significantly increased Ca, Mg, K, and P uptake as well as K content in roots. In vitro experiments using the Pikovskaya method showed that the EPS was able to solubilize phosphorus. Consistent with the retention of metals in roots and a reduction in shoots, our data revealed a significant decrease in metal translocation factors (TFs) in the plants inoculated with the EPS. These results suggest a beneficial effect of the rhizobacterial EPS on plant growth and abiotic stress mitigation. In addition, the data suggest that the reduced levels of trace metals in plants exposed to P. ultramafica STM10279T are due to metal chelation by the EPS. Further investigations are needed to firmly demonstrate whether this EPS could be used as a biostimulant for plant growth and adaptation to ultramafic soils.
Keywords: PGPR; Paraburkholderia; biostimulant; exopolysaccharides; phosphate solubilization; plant metal alleviation; ultramafic soil.
Copyright © 2024 Bourles, Pierre, Amir, Le Floc’h, Chalkiadakis, Médevielle, Jourand, Michaud, Burtet-Sarramégna and Guentas.
Conflict of interest statement
Author EC is employed by BIOTECAL, Marine Biotechnology Company, New Caledonia. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Amir H., Ducousso M. (2010). “Les bactéries et les champignons du sol sur roches ultramafiques,” in Mines et environnement en Nouvelle-Calédonie : les milieux sur substrats ultramafiques et leur restauration. (Nouméa: IAC; ), 129–145. Available at: http://www.documentation.ird.fr/hor/fdi:010057561.
-
- Bashan Y., Huang P., Kloepper J. W., de-Bashan L. (2017). A proposal for avoiding fresh-weight measurements when reporting the effect of plant growth-promoting (rhizo) bacteria on growth promotion of plants. Biol. Fertil. Soils 53, 1–2. doi: 10.1007/s00374-016-1153-1 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

