A scoping review on active vs. passive range of motion approaches to treat heterotopic ossification at the elbow
- PMID: 38903480
- PMCID: PMC11188409
- DOI: 10.3389/fresc.2024.1327417
A scoping review on active vs. passive range of motion approaches to treat heterotopic ossification at the elbow
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this scoping review is to synthesize and clarify literature on the effectiveness of active and passive range of motion therapy techniques to address range of motion in people with heterotopic ossification (HO), and to provide guidance to therapists in clinical decision-making based on current evidence.
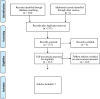
Method: To find articles that included therapeutic interventions to maintain or improve range of motion in people with heterotopic ossification, the authors searched the following databases: Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, PubMed, CINAHL, PsychINFO, Web of Science, and OTSeeker. To ensure that the search was comprehensive, the authors also searched Burns and Trauma, Burns Journal, Burns Open, and the Journal of Hand Therapy. Searches were limited to peer-reviewed articles published in the English language. No publication date limits were set. The Physiotherapy Evidence Database PEDro scale was utilized to measure the validity of the methodological quality of each article.
Results: Five studies met the inclusion criteria.. Two studies emphasized that passive range of motion was effective in less than 50% of their subjects, while the other three studies utilized active range of motion only, reporting 50% of patients did not require surgery.
Discussion/conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to determine effective therapeutic management of HO and the literature that does exist is contradictory and inconclusive. Future research is necessary to determine if any effectiveness of manual therapeutic approaches exists for patients with HO.
Keywords: elbow contracture; heterotopic ossification; joint contracture; occupational therapy; physical therapy.
© 2024 Siegel, Smith, Stark, Burns and Dionne.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Role of Kinesiotherapy in the Prevention of Heterotopic Ossification: A Systematic Review.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023 Feb 1;102(2):110-119. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002043. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 35512120
-
Physiotherapy rehabilitation after total knee or hip replacement: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(8):1-91. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074477 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotopic ossification of the elbow treated with surgical resection: risk factors, bony ankylosis, and complications.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jul;472(7):2269-75. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3591-0. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24711127 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotopic Ossification Prophylaxis Following Operative Fixation of Acetabular Fractures: A Systematic Review.Surg Technol Int. 2022 May 19;40:369-385. doi: 10.52198/22.STI.40.OS1543. Surg Technol Int. 2022. PMID: 35157298
Cited by
-
When Bone Forms Where It Shouldn't: Heterotopic Ossification in Muscle Injury and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 4;26(15):7516. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157516. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous