The clinical management of hepatic sarcoidosis: A systematic review
- PMID: 38903487
- PMCID: PMC11187478
- DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.13076
The clinical management of hepatic sarcoidosis: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Hepatic sarcoidosis is an uncommon clinical condition in which clear recommendations are lacking in its treatment. We aimed to review systematically the literature on hepatic sarcoidosis treatment to guide clinicians.
Methods: Using MEDLINE, PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar databases, we searched original articles on clinical studies reporting the outcome of adult hepatic sarcoidosis patients following treatment with various pharmacological agents. The primary end point was focused on assessing symptomatic relief and biochemical improvement posttreatment.
Results: Out of 614 retrieved references, 34 published studies were eligible, providing data for a total of 268 patients with hepatic sarcoidosis. First-line therapy with corticosteroids alone was reported in 187 patients, whilst ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) was used in 40 patients. Symptomatic and biochemical responses were reported among 113(60.4%) and 80(42.8%) cases of corticosteroids respectively, whereas UDCA showed a complete response in 23(57.5%) patients. Second-line therapy was used in steroid-refractory cases, with most cases being reported for azathioprine (n = 32) and methotrexate (n = 28). Notably, 15(46.9%) and 11(39.2%) patients showed both clinical and biochemical responses respectively. Biological therapy including anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) was used as third line therapy in twelve cases with a 72.7% symptomatic and biochemical response rate each.
Conclusion: The quality of evidence for the treatment of hepatic sarcoidosis was poor. Nevertheless, it appears that corticosteroid or UDCA may be utilized as first-line therapy. For cases that are refractory to corticosteroids, steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents and anti-TNF have shown some promising results, but further high-quality studies are required.
Keywords: anti‐TNF, Ursodeoxycholic acid; azathioprine; corticosteroids; hepatic sarcoidosis; methotrexate.
© 2024 The Author(s). JGH Open published by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
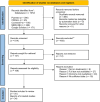

 biochemical improvement,
biochemical improvement,  symptomatic improvement. Abbreviations: CS, corticosteroids; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid. (b)
symptomatic improvement. Abbreviations: CS, corticosteroids; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid. (b)  symptomatic improvement,
symptomatic improvement,  biochemical improvement. Abbreviations: AZA, azathioprine; IFX, infliximab; MTX, methotrexate.
biochemical improvement. Abbreviations: AZA, azathioprine; IFX, infliximab; MTX, methotrexate.
Similar articles
-
Hepatic sarcoidosis: Clinical characteristics and outcome.JHEP Rep. 2021 Sep 3;3(6):100360. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100360. eCollection 2021 Dec. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34765958 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Clinical Studies on the Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) and Janus Kinase/Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (JAK/STAT) Antibody Therapies in Refractory Cutaneous Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 8;15(9):e44901. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44901. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37818515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Practices and Emerging Therapies to Optimize Heart Failure Management in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 9;16(8):e66515. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66515. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39252727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacotherapeutic management of pulmonary sarcoidosis.Am J Respir Med. 2003;2(4):311-20. doi: 10.1007/BF03256659. Am J Respir Med. 2003. PMID: 14719997 Review.
-
Sarcoidosis of the liver: to treat or not to treat?Neth J Med. 2012 Oct;70(8):349-56. Neth J Med. 2012. PMID: 23065982 Review.
References
-
- Culver DA. Sarcoidosis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2012; 32: 487–511. - PubMed
-
- Ebert EC, Kierson M, Hagspiel KD. Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of sarcoidosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008; 103: 3184–3192 quiz 93. - PubMed
-
- Deutsch‐Link S, Fortuna D, Weinberg EM. A comprehensive review of hepatic sarcoid. In: Seminars in Liver Disease. Thieme Medical Publishers, New York; 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

