Effect of quercetin against pilocarpine-induced epilepsy in mice
- PMID: 38903552
- PMCID: PMC11186541
- DOI: 10.4103/JAPTR.JAPTR_496_23
Effect of quercetin against pilocarpine-induced epilepsy in mice
Abstract
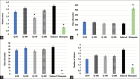
Globally, an estimated 50 million people are affected by epilepsy, a persistent, noncommunicable neurological ailment. Quercetin (QR) is a prevalent flavonoid substance extensively dispersed throughout agricultural life. In a pilocarpine (PILO)-induced epilepsy model in mice, this investigation aimed to determine whether QR has an antiepileptic effect and explore its putative mechanism of action. Fifty mice were allocated into seven groups, with six in every group. The first group received physiological saline, the second group was given diazepam (1 mg/kg), and four groups were administered QR at 50, 100, 150, and 200 mg/kg, respectively. The seventh group (the induction group) received normal saline. After 30 min, all groups were injected intraperitoneally with PILO. The impact of QR on motor coordination was assessed using the rotarod test, while measures such as latency to first seizure, generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTCS), number of convulsions, and mortality were recorded. Serum samples were collected through the retro-orbital route to measure prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) levels. QR showed no significant difference in motor impairment, but increased duration until the initial seizure occurred and declined the mortality rate, duration of GTCS, and incidence of convulsions. All doses of QR significantly reduced PGE2 levels (P ≤ 0.05). However, QR's effect on IL-1β reduction was statistically insignificant (P > 0.05). QR's capacity to inhibit PILO-induced epilepsy by decreasing IL-1 and PGE2 levels is supported by this study. The results of this work indicate that QR could have a function to treat acute epilepsy.
Keywords: Epilepsy; interleukin 1 beta; pilocarpine; prostaglandin E2; quercetin.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Falco Walter J. Epilepsy-definition, classification, pathophysiology, and epidemiology. Semin Neurol. 2020;40:617–23. - PubMed
-
- Hunter MB, Yoong M, Sumpter RE, Verity K, Shetty J, McLellan A, et al. Incidence of early-onset epilepsy: A prospective population-based study. Seizure. 2020;75:49–54. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RS, Bonner AM. The revised definition and classification of epilepsy for neurodiagnostic technologists. Neurodiagn J. 2018;58:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Neuroepidemiology EB. The epidemiology of epilepsy. 2020 Available from: https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/503831 . [Last accessed on 2023 Feb 17] - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

