Prevalence, Characteristics, and Impact on Prognosis of Aortic Stenosis in Patients With Cardiac Amyloidosis
- PMID: 38904242
- PMCID: PMC11255711
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.034723
Prevalence, Characteristics, and Impact on Prognosis of Aortic Stenosis in Patients With Cardiac Amyloidosis
Abstract
Background: Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is frequently found in older patients with aortic stenosis (AS). However, the prevalence of AS among patients with CA is unknown. The objective was to study the prevalence and prognostic impact of AS among patients with CA.
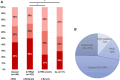
Methods and results: We conducted a retrospective analysis of a prospective registry comprising 976 patients with native aortic valves who were confirmed with wild type transthyretin amyloid (ATTRwt), hereditary variant transthyretin amyloid (ATTRv), or immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) CA. CA patients' echocardiograms were re-analyzed focusing on the aortic valve. Multivariable Cox regression analysis was performed to assess the mortality risk associated with moderate or greater AS in ATTRwt CA. The crude prevalence of AS among patients with CA was 26% in ATTRwt, 8% in ATTRv, and 5% in AL. Compared with population-based controls, all types of CA had higher age- and sex-standardized rate ratios (SRRs) of having any degree of AS (AL: SRR, 2.62; 95% Confidence Interval (CI) [1.09-3.64]; ATTRv: SRR, 3.41; 95%CI [1.64-4.60]; ATTRwt: SRR, 10.8; 95%CI [5.25-14.53]). Compared with hospital controls, only ATTRwt had a higher SRR of having any degree of AS (AL: SRR, 0.97, 95%CI [0.56-1.14]; ATTRv: SRR, 1.27; 95%CI [0.85-1.44]; ATTRwt: SRR, 4.01; 95%CI [2.71-4.54]). Among patients with ATTRwt, moderate or greater AS was not associated with increased all-cause death after multivariable adjustment (hazard ratio, 0.71; 95%CI [0.42-1.19]; P=0.19).
Conclusions: Among patients with CA, ATTRwt but not ATTRv or AL is associated with a higher prevalence of patients with AS compared with hospital controls without CA, even after adjusting for age and sex. In our population, having moderate or greater AS was not associated with a worse outcome in patients with ATTRwt.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; cardiac amyloidosis; echocardiography; prognosis; transthyretin.
Figures




References
-
- Cornwell GG III, Murdoch WL, Kyle RA, Westermark P, Pitkanen P. Frequency and distribution of senile cardiovascular amyloid. A clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Med. 1983;75:618–623. - PubMed
-
- Tanskanen M, Peuralinna T, Polvikoski T, Notkola IL, Sulkava R, Hardy J, Singleton A, Kiuru‐Enari S, Paetau A, Tienari PJ, et al. Senile systemic amyloidosis affects 25% of the very aged and associates with genetic variation in alpha2‐macroglobulin and tau: a population‐based autopsy study. Ann Med. 2008;40:232–239. doi: 10.1080/07853890701842988 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Longhi S, Lorenzini M, Gagliardi C, Milandri A, Marzocchi A, Marrozzini C, Saia F, Ortolani P, Biagini E, Guidalotti PL, et al. Coexistence of degenerative aortic stenosis and wild‐type transthyretin‐related cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9:325–327. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.04.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castaño A, Narotsky DL, Hamid N, Khalique OK, Morgenstern R, DeLuca A, Rubin J, Chiuzan C, Nazif T, Vahl T, et al. Unveiling transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis and its predictors among elderly patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:2879–2887. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx350 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

