Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry (REMS) in the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis: state of the art
- PMID: 38904870
- PMCID: PMC11192661
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-024-02784-w
Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry (REMS) in the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis: state of the art
Abstract
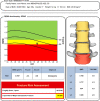
Radiofrequency Echographic Multi Spectrometry (REMS) is a radiation-free, portable technology, which can be used for the assessment and monitoring of osteoporosis at the lumbar spine and femoral neck and may facilitate wider access to axial BMD measurement compared with standard dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA).There is a growing literature demonstrating a strong correlation between DXA and REMS measures of BMD and further work supporting 5-year prediction of fracture using the REMS Fragility Score, which provides a measure of bone quality (in addition to the quantitative measure of BMD).The non-ionising radiation emitted by REMS allows it to be used in previously underserved populations including pregnant women and children and may facilitate more frequent measurement of BMD.The portability of the device means that it can be deployed to measure BMD for frail patients at the bedside (avoiding the complications in transfer and positioning which can occur with DXA), in primary care, the emergency department, low-resource settings and even at home.The current evidence base supports the technology as a useful tool in the management of osteoporosis as an alternative to DXA.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Fracture; Osteoporosis; Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry (REMS); Screening.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JYR, NAD, OB, NB, CCo, ADP, PH, TG, JMK, AK, RM, RPR, ST, RR, NCH, MLB have no competing interests to declare. CCa has received speaker fees from FAES farma, Asofarma and Novartis. NRF reports speaker’s fees from Viatris and travel bursaries from Pfizer and Eli Lilly. NV reports personal fees from MYLAN, FIDIA, IBSA, Pfizer, Sanofi.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

