BOLERO-5: a phase II study of everolimus and exemestane combination in Chinese post-menopausal women with ER + /HER2- advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 38904918
- PMCID: PMC11192707
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01027-8
BOLERO-5: a phase II study of everolimus and exemestane combination in Chinese post-menopausal women with ER + /HER2- advanced breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The global BOLERO-2 trial established the efficacy and safety of combination everolimus (EVE) and exemestane (EXE) in the treatment of estrogen receptor positive (ER +), HER2-, advanced breast cancer (ABC). BOLERO-5 investigated this combination in a Chinese population (NCT03312738).
Methods: BOLERO-5 is a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo controlled, phase II trial comparing EVE (10 mg/day) or placebo (PBO) in combination with EXE (25 mg/day). The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) per investigator assessment. Secondary endpoints included PFS per blinded independent review committee (BIRC), overall survival (OS), overall response rate (ORR), clinical benefit rate (CBR), pharmacokinetics, and safety.
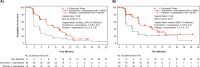
Results: A total of 159 patients were randomized to EVE + EXE (n = 80) or PBO + EXE (n = 79). By investigator assessment, treatment with EVE + EXE prolonged median PFS by 5.4 months (HR 0.52; 90% CI 0.38, 0.71), from 2.0 months (PBO + EXE; 90% CI 1.9, 3.6) to 7.4 months (EVE + EXE; 90% CI 5.5, 9.0). Similar results were observed following assessment by BIRC, with median PFS prolonged by 4.3 months. Treatment with EVE + EXE was also associated with improvements in ORR and CBR. No new safety signals were identified in BOLERO-5, with the incidence of adverse events in Chinese patients consistent with the safety profile of both drugs.
Conclusion: The efficacy and safety results of BOLERO-5 validate the findings from BOLERO-2, and further support the use of EVE + EXE in Chinese post-menopausal women with ER + , HER2- ABC. NCT03312738, registered 18 October 2017.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K. A., K. Slimane, Y. Q., and Y. L. are employees of Novartis. All other authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous