The Bioinformatic Applications of Hi-C and Linked Reads
- PMID: 38905513
- PMCID: PMC11580686
- DOI: 10.1093/gpbjnl/qzae048
The Bioinformatic Applications of Hi-C and Linked Reads
Abstract
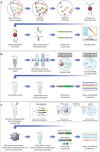
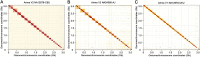
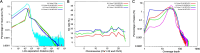
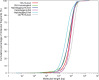
Long-range sequencing grants insight into additional genetic information beyond what can be accessed by both short reads and modern long-read technology. Several new sequencing technologies, such as "Hi-C" and "Linked Reads", produce long-range datasets for high-throughput and high-resolution genome analyses, which are rapidly advancing the field of genome assembly, genome scaffolding, and more comprehensive variant identification. In this review, we focused on five major long-range sequencing technologies: high-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), 10X Genomics Linked Reads, haplotagging, transposase enzyme linked long-read sequencing (TELL-seq), and single- tube long fragment read (stLFR). We detailed the mechanisms and data products of the five platforms and their important applications, evaluated the quality of sequencing data from different platforms, and discussed the currently available bioinformatics tools. This work will benefit the selection of appropriate long-range technology for specific biological studies.
Keywords: Genome assembly; Hi-C; Linked Reads; Long-range NGS reads; Quality assessment.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press and Science Press on behalf of the Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences / China National Center for Bioinformation and Genetics Society of China.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

