Toward developing human organs via embryo models and chimeras
- PMID: 38906095
- PMCID: PMC11239105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.027
Toward developing human organs via embryo models and chimeras
Abstract
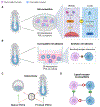
Developing functional organs from stem cells remains a challenging goal in regenerative medicine. Existing methodologies, such as tissue engineering, bioprinting, and organoids, only offer partial solutions. This perspective focuses on two promising approaches emerging for engineering human organs from stem cells: stem cell-based embryo models and interspecies organogenesis. Both approaches exploit the premise of guiding stem cells to mimic natural development. We begin by summarizing what is known about early human development as a blueprint for recapitulating organogenesis in both embryo models and interspecies chimeras. The latest advances in both fields are discussed before highlighting the technological and knowledge gaps to be addressed before the goal of developing human organs could be achieved using the two approaches. We conclude by discussing challenges facing embryo modeling and interspecies organogenesis and outlining future prospects for advancing both fields toward the generation of human tissues and organs for basic research and translational applications.
Keywords: blastocyst complementation; extraembryonic endoderm cells; hypoblast stem cells; interspecies chimeras; interspecies organogenesis; organ engineering; pluripotent stem cells; stem cell-based embryo models; trophoblast stem cells.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
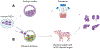


References
-
- Rafat M, Jabbarvand M, Sharma N, Xeroudaki M, Tabe S, Omrani R, Thangavelu M, Mukwaya A, Fagerholm P, Lennikov A, et al. (2023). Bioengineered corneal tissue for minimally invasive vision restoration in advanced keratoconus in two clinical cohorts. Nat Biotechnol 41, 70–81. 10.1038/s41587-022-01408-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS129850/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS127983/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM143297/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM138565/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD105349/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS113518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD105126/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD109635/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD105192/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD103627/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG011996/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD100931/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

