2'-O-methylation at internal sites on mRNA promotes mRNA stability
- PMID: 38906115
- PMCID: PMC11196006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.04.011
2'-O-methylation at internal sites on mRNA promotes mRNA stability
Abstract
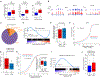
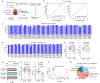
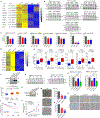
2'-O-methylation (Nm) is a prominent RNA modification well known in noncoding RNAs and more recently also found at many mRNA internal sites. However, their function and base-resolution stoichiometry remain underexplored. Here, we investigate the transcriptome-wide effect of internal site Nm on mRNA stability. Combining nanopore sequencing with our developed machine learning method, NanoNm, we identify thousands of Nm sites on mRNAs with a single-base resolution. We observe a positive effect of FBL-mediated Nm modification on mRNA stability and expression level. Elevated FBL expression in cancer cells is associated with increased expression levels for 2'-O-methylated mRNAs of cancer pathways, implying the role of FBL in post-transcriptional regulation. Lastly, we find that FBL-mediated 2'-O-methylation connects to widespread 3' UTR shortening, a mechanism that globally increases RNA stability. Collectively, we demonstrate that FBL-mediated Nm modifications at mRNA internal sites regulate gene expression by enhancing mRNA stability.
Keywords: 2′-O-methylation; CPSF7; FBL; RNA stability; alternative polyadenylation; epitranscriptomics; mRNA modification; machine learning; nanopore; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM138407/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA180995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM108569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155632/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025194/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025120/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA278832/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA256741/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133254/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA208257/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM125632/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

