Asciminib antagonizes transplantable BCR::ABL1-positive lymphoid blast crisis in vivo by targeting malignant stem cells
- PMID: 38906962
- PMCID: PMC11286509
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-024-02320-9
Asciminib antagonizes transplantable BCR::ABL1-positive lymphoid blast crisis in vivo by targeting malignant stem cells
Abstract
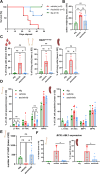
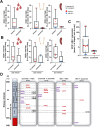
Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) lymphoid blast crisis (BC), emanating from chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), is a fatal disease with limited treatment options. Asciminib (ABL001) is a novel selective allosteric inhibitor of the ABL kinase with high efficacy against TKI-resistant BCR::ABL1. In this study, we demonstrate significant suppression of an aggressive B-lymphoblastic disease and restoration of normal hematopoiesis in an inducible transgenic mouse model of p210-BCR::ABL1-positive CML-BC. Molecularly, asciminib treatment significantly reduced BCR::ABL1 transcripts to background levels, demonstrating its ability to suppress BCR::ABL1-induced disease. Furthermore, asciminib treatment normalized the long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cell (LT-HSC) population in the BM, suggesting the selective targeting of malignant LT-HSCs. This was supported by secondary transplantation experiments, resulting in absence of BC in a proportion of mice. Importantly, none of the secondary transplanted mice that received further asciminib treatment developed leukemia. Sanger sequencing of the BCR::ABL1 myristoyl pocket region of both treatment-naïve and treated mice demonstrated a high mutational load. However, there was no indication of asciminib-specific mutations. These promising findings highlight the potential of asciminib as a drug that targets BC stem cells and as an alternative stand-alone or combinatorial therapy for first-line treatment of CML BC or Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
SK received research funding from Novartis for this preclinical study, received consulting fees, honoraria, and travel/accommodation support from Novartis, and reports participation on advisory boards for Novartis. THB served as consultant/speaker for Synlab, Incyte, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche and received research support from Novartis and Pfizer.
Figures
References
-
- Pfeifer H, Wassmann B, Pavlova A, Wunderle L, Oldenburg J, Binckebanck A, et al. Kinase domain mutations of BCR-ABL frequently precede imatinib-based therapy and give rise to relapse in patients with de novo Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). Blood. 2007;110:727–34. 10.1182/blood-2006-11-052373 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

