Orpinolide disrupts a leukemic dependency on cholesterol transport by inhibiting OSBP
- PMID: 38907113
- PMCID: PMC11782089
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-024-01614-4
Orpinolide disrupts a leukemic dependency on cholesterol transport by inhibiting OSBP
Abstract
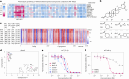
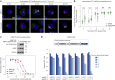
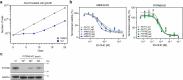
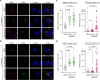
Metabolic alterations in cancer precipitate in associated dependencies that can be therapeutically exploited. To meet this goal, natural product-inspired small molecules can provide a resource of invaluable chemotypes. Here, we identify orpinolide, a synthetic withanolide analog with pronounced antileukemic properties, via orthogonal chemical screening. Through multiomics profiling and genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screens, we identify that orpinolide disrupts Golgi homeostasis via a mechanism that requires active phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate signaling at the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi membrane interface. Thermal proteome profiling and genetic validation studies reveal the oxysterol-binding protein OSBP as the direct and phenotypically relevant target of orpinolide. Collectively, these data reaffirm sterol transport as a therapeutically actionable dependency in leukemia and motivate ensuing translational investigation via the probe-like compound orpinolide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: G.E.W. and G.S.-F. are scientific founders and shareholders of Proxygen and Solgate. G.E.W. is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Nexo Therapeutics. The laboratories of G.E.W. and G.S.-F. received research funding from Pfizer. C.M.-R. is part of the Scientific Advisory Board of Nostrum Biodiscovery. The C.M.-R. lab receives research funding from Aelin Therapeutics and Almirall. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Hanahan, D. & Weinberg, R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell144, 646–674 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wang, Y. et al. Rapid diagnosis and prognosis of de novo acute myeloid leukemia by serum metabonomic analysis. J. Proteome Res.12, 4393–4401 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Newman, D. J. & Cragg, G. M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod.83, 770–803 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P32125/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
- 851478/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- P 32125/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
- P 31690/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
- P31690/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

