Amplifying colorectal cancer progression: impact of a PDIA4/SP1 positive feedback loop by circPDIA4 sponging miR-9-5p
- PMID: 38907517
- PMCID: PMC11523275
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0112
Amplifying colorectal cancer progression: impact of a PDIA4/SP1 positive feedback loop by circPDIA4 sponging miR-9-5p
Abstract
Objective: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a prevalent malignant tumor with a high fatality rate. CircPDIA4 has been shown to have a vital role in cancer development by acting as a facilitator. Nevertheless, the impact of the circPDIA4/miR-9-5p/SP1 axis on development of CRC has not been studied.
Methods: Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays were used to analyze gene expression. The CCK-8 assay was used to assess cell growth. The Transwell assay was used to detect invasion and migration of cells. The luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation tests were used to determine if miR-9-5p and circPDIA4 (or SP1) bind to one another. An in vivo assay was used to measure tumor growth.
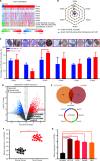
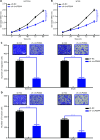
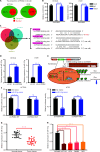
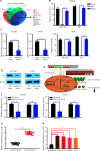
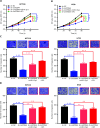
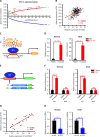
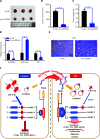
Results: It was shown that circPDIA4 expression was greater in CRC cell lines and tissues than healthy cell lines and tissues. CircPDIA4 knockdown prevented the invasion, migration, and proliferation of cells in CRC. Additionally, the combination of circPDIA4 and miR-9-5p was confirmed, as well as miR-9-5p binding to SP1. Rescue experiments also showed that the circPDIA4/miR-9-5p/SP1 axis accelerated the development of CRC. In addition, SP1 combined with the promoter region of circPDIA4 and induced circPDIA4 transcription. CircPDIA4 was shown to facilitate tumor growth in an in vivo assay.
Conclusions: The circPDIA4/miR-9-5p/SP1 feedback loop was shown to aggravate CRC progression. This finding suggests that the ceRNA axis may be a promising biomarker for CRC patient treatment.
Keywords: CircRNA; PDIA4; SP1; colorectal cancer; positive feedback loop.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription factor SP1-induced microRNA-146b-3p facilitates the progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer via regulating FAM107A.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119398. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119398. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33831429
-
Circular RNA circ_0058123 Targets the miR-939-5p/RAC1 Pathway to Promote the Development of Colorectal Cancer.Biochem Genet. 2024 Jun;62(3):1485-1501. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10485-8. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37642813
-
Circular RNA circ_0007142 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via miR-455-5p/SGK1 axis in colorectal cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2021 Jan 1;32(1):22-33. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000992. Anticancer Drugs. 2021. PMID: 32889894
-
lncRNA UCA1 induced by SP1 and SP3 forms a positive feedback loop to facilitate malignant phenotypes of colorectal cancer via targeting miR-495.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119569. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119569. Epub 2021 May 4. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33961855
-
miR-138-5p inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer via regulating SP1/LGR5 axis.Cell Biol Int. 2023 Jan;47(1):273-282. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11926. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Cell Biol Int. 2023. PMID: 36317454
References
-
- Keum N, Giovannucci E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:713–32. - PubMed
-
- Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB. Colorectal cancer. Lancet (London, England) 2019;394:1467–80. - PubMed
-
- Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. JAMA. 2021;325:669–85. - PubMed
-
- Li N, Lu B, Luo C, Cai J, Lu M, Zhang Y, et al. Incidence, mortality, survival, risk factor and screening of colorectal cancer: a comparison among China, Europe, and northern America. Cancer Lett. 2021;522:255–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
