Ferumoxtran-10-enhanced MRI for pre-operative metastatic lymph node detection in pancreatic, duodenal, or periampullary adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38907886
- PMCID: PMC11557713
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-10838-w
Ferumoxtran-10-enhanced MRI for pre-operative metastatic lymph node detection in pancreatic, duodenal, or periampullary adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: To assess 3-Tesla (3-T) ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO)-enhanced MRI in detecting lymph node (LN) metastases for resectable adenocarcinomas of the pancreas, duodenum, or periampullary region in a node-to-node validation against histopathology.
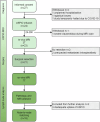
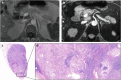
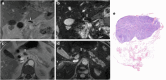
Methods: Twenty-seven consecutive patients with a resectable pancreatic, duodenal, or periampullary adenocarcinoma were enrolled in this prospective single expert centre study. Ferumoxtran-10-enhanced 3-T MRI was performed pre-surgery. LNs found on MRI were scored for suspicion of metastasis by two expert radiologists using a dedicated scoring system. Node-to-node matching from in vivo MRI to histopathology was performed using a post-operative ex vivo 7-T MRI of the resection specimen. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated using crosstabs.
Results: Eighteen out of 27 patients (median age 65 years, 11 men) were included in the final analysis (pre-surgery withdrawal n = 4, not resected because of unexpected metastases peroperatively n = 2, and excluded because of inadequate contrast-agent uptake n = 3). On MRI 453 LNs with a median size of 4.0 mm were detected, of which 58 (13%) were classified as suspicious. At histopathology 385 LNs with a median size of 5.0 mm were found, of which 45 (12%) were metastatic. For 55 LNs node-to-node matching was possible. Analysis of these 55 matched LNs, resulted in a sensitivity and specificity of 83% (95% CI: 36-100%) and 92% (95% CI: 80-98%), respectively.
Conclusion: USPIO-enhanced MRI is a promising technique to preoperatively detect and localise LN metastases in patients with pancreatic, duodenal, or periampullary adenocarcinoma.
Clinical relevance statement: Detection of (distant) LN metastases with USPIO-enhanced MRI could be used to determine a personalised treatment strategy that could involve neoadjuvant or palliative chemotherapy, guided resection of distant LNs, or targeted radiotherapy.
Registration: The study was registered on clinicaltrials.gov NCT04311047. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04311047?term=lymph+node&cond=Pancreatic+Cancer&cntry=NL&draw=2&rank=1 .
Key points: LN metastases of pancreatic, duodenal, or periampullary adenocarcinoma cannot be reliably detected with current imaging. This technique detected LN metastases with a sensitivity and specificity of 83% and 92%, respectively. MRI with ferumoxtran-10 is a promising technique to improve preoperative staging in these cancers.
Keywords: Duodenal cancer; Lymph node metastasis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Pancreatic cancer; Periampullary cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Slidell MB, Chang DC, Cameron JL et al (2008) Impact of total lymph node count and lymph node ratio on staging and survival after pancreatectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a large, population-based analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 15:165–174 - PubMed
-
- Wellner UF, Shen Y, Keck T, Jin W, Xu Z (2017) The survival outcome and prognostic factors for distal cholangiocarcinoma following surgical resection: a meta-analysis for the 5-year survival. Surg Today 47:271–279 - PubMed
-
- Lowe MC, Coban I, Adsay NV et al (2009) Important prognostic factors in adenocarcinoma of the ampulla of Vater. Am Surg 75:754–760 - PubMed
-
- UICC (2016) TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley, New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

