Short-Read RNA-Seq
- PMID: 38907923
- PMCID: PMC12125952
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3918-4_17
Short-Read RNA-Seq
Abstract
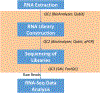
RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) has emerged as a powerful and versatile tool for the comprehensive analysis of transcriptomes and has been widely used to investigate gene expression, copy number variation, alternative splicing, and novel transcript discovery. This chapter outlines the methodology for conducting short-read RNA-Seq, starting from RNA enrichment to library preparation and sequencing. Throughout the chapter, practical tips and best practices are provided to guide researchers in order to optimize each step of the RNA-Seq workflow. Multiple quality control steps throughout the workflow that are critical to obtain high-quality RNA-Seq data are also discussed.
Keywords: Library preparation; RNA-Seq; Short-read sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

