Interactomic exploration of LRRC8A in volume-regulated anion channels
- PMID: 38909013
- PMCID: PMC11193767
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-02032-0
Interactomic exploration of LRRC8A in volume-regulated anion channels
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Interactomic exploration of LRRC8A in volume-regulated anion channels.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Aug 29;10(1):387. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02123-y. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39209805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
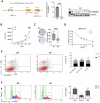
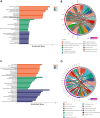
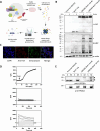
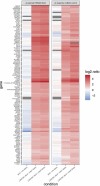
Ion channels are critical in enabling ion movement into and within cells and are important targets for pharmacological interventions in different human diseases. In addition to their ion transport abilities, ion channels interact with signalling and scaffolding proteins, which affects their function, cellular positioning, and links to intracellular signalling pathways. The study of "channelosomes" within cells has the potential to uncover their involvement in human diseases, although this field of research is still emerging. LRRC8A is the gene that encodes a crucial protein involved in the formation of volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs). Some studies suggest that LRRC8A could be a valuable prognostic tool in different types of cancer, serving as a biomarker for predicting patients' outcomes. LRRC8A expression levels might be linked to tumour progression, metastasis, and treatment response, although its implications in different cancer types can be varied. Here, publicly accessible databases of cancer patients were systematically analysed to determine if a correlation between VRAC channel expression and survival rate exists across distinct cancer types. Moreover, we re-evaluated the impact of LRRC8A on cellular proliferation and migration in colon cancer via HCT116 LRRC8A-KO cells, which is a current topic of debate in the literature. In addition, to investigate the role of LRRC8A in cellular signalling, we conducted biotin proximity-dependent identification (BioID) analysis, revealing a correlation between VRAC channels and cell-cell junctions, mechanisms that govern cellular calcium homeostasis, kinases, and GTPase signalling. Overall, this dataset improves our understanding of LRRC8A/VRAC and explores new research avenues while identifying promising therapeutic targets and promoting inventive methods for disease treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LRRC8A homohexameric channels poorly recapitulate VRAC regulation and pharmacology.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):C293-C303. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00454.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33356947 Free PMC article.
-
Volume-regulated chloride channel regulates cell proliferation and is involved in the possible interaction between TMEM16A and LRRC8A in human metastatic oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 15;895:173881. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173881. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33476655
-
TTYH1 and TTYH2 Serve as LRRC8A-Independent Volume-Regulated Anion Channels in Cancer Cells.Cells. 2019 Jun 9;8(6):562. doi: 10.3390/cells8060562. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31181821 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics and Physiology of the Volume-Regulated Anion Channel (VRAC)/Volume-Sensitive Outwardly Rectifying Anion Channel (VSOR).Pflugers Arch. 2016 Mar;468(3):371-83. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1781-6. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26739710 Review.
-
Molecular Biology and Physiology of Volume-Regulated Anion Channel (VRAC).Curr Top Membr. 2018;81:177-203. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Curr Top Membr. 2018. PMID: 30243432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico pan-cancer analysis of VRAC subunits and their prognostic roles in human cancers.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 11;15(1):12388. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97078-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40216864 Free PMC article.
-
LRRC8A/PKC/FLNA pathway activation is detrimental to colon cancer patients.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jun 27;25(1):138. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01650-w. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40576693
-
LRRC8A-containing anion channels promote glioblastoma proliferation via a WNK1/mTORC2-dependent mechanism.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 6:2025.02.02.636139. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.02.636139. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975357 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Recent insights on the impact of SWELL1 on metabolic syndromes.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 21;16:1552176. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1552176. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40191429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boi-Ogi-To, a Traditional Japanese Kampo Medicine, Promotes Cellular Excretion of Chloride and Water by Activating Volume-Sensitive Outwardly Rectifying Anion Channels.FASEB J. 2025 May 15;39(9):e70573. doi: 10.1096/fj.202403278R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40341625 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- DOR (Dotazione Ordinaria della Ricerca dipartimentale) projects - Calls 2021-2022-2023/Università degli Studi di Padova (University of Padova)
- SEED-PRID project 2021 entitled "Setting up in vivo interactome for cancer research"/Università degli Studi di Padova (University of Padova)
- BIRD-PRID, grant number BIRD239198/23/Università degli Studi di Padova (University of Padova)
- PRIN, grant number 2022ZY7ATN/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca (Ministry of Education, University and Research)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

