An EEG & eye-tracking dataset of ALS patients & healthy people during eye-tracking-based spelling system usage
- PMID: 38909069
- PMCID: PMC11193709
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03501-y
An EEG & eye-tracking dataset of ALS patients & healthy people during eye-tracking-based spelling system usage
Abstract
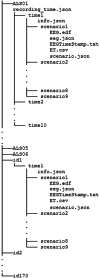
This research presents a dataset consisting of electroencephalogram and eye tracking recordings obtained from six patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in a locked-in state and one hundred seventy healthy individuals. The ALS patients exhibited varying degrees of disease progression, ranging from partial mobility and weakened speech to complete paralysis and loss of speech. Despite these physical impairments, the ALS patients retained good eye function, which allowed them to use a virtual keyboard for communication. Data from ALS patients was recorded multiple times at their homes, while data from healthy individuals was recorded once in a laboratory setting. For each data recording, the experimental design involved nine recording sessions per participant, each corresponding to a common human action or demand. This dataset can serve as a valuable benchmark for several applications, such as improving spelling systems with brain-computer interfaces, investigating motor imagination, exploring motor cortex function, monitoring motor impairment progress in patients undergoing rehabilitation, and studying the effects of ALS on cognitive and motor processes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




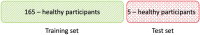

Similar articles
-
A dataset of EEG and EOG from an auditory EOG-based communication system for patients in locked-in state.Sci Data. 2021 Jan 11;8(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00789-4. Sci Data. 2021. PMID: 33431874 Free PMC article.
-
Brain computer interface with the P300 speller: Usability for disabled people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2018 Jan;61(1):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2018. PMID: 29024794
-
Brain-machine interface (BMI) in paralysis.Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2015 Feb;58(1):9-13. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2014.11.002. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2015. PMID: 25623294
-
Electrophysiological correlates of neurodegeneration in motor and non-motor brain regions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-implications for brain-computer interfacing.J Neural Eng. 2018 Aug;15(4):041003. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aabfa5. Epub 2018 Apr 20. J Neural Eng. 2018. PMID: 29676287 Review.
-
Brain-computer interfaces for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Handb Clin Neurol. 2020;168:33-38. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63934-9.00004-4. Handb Clin Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32164864 Review.
Cited by
-
A simultaneous EEG and eye-tracking dataset for remote sensing object detection.Sci Data. 2025 Apr 17;12(1):651. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04995-w. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40246854 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Portable Dry Electrode EEG: Architecture and Applications in Brain-Computer Interfaces.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Aug 21;25(16):5215. doi: 10.3390/s25165215. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel accurate classification system developed using order transition pattern feature engineering technique with physiological signals.Sci Rep. 2025 May 1;15(1):15278. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00071-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40312463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brownlee A, Bruening LM. Methods of communication at end of life for the person with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Top.Lang. Disord. 2012;32(2):168–185. doi: 10.1097/TLD.0b013e31825616ef. - DOI
-
- Calvo A, et al. Eye Tracking Impact on Quality-of-Life of ALS Patients. 11th International Conference on Computers Helping People with Special Needs, Linz (AT). 2008;5105:70–77. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-70540-6_9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

