β-hydroxybutyrate resensitizes colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by suppressing H3K79 methylation in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 38910244
- PMCID: PMC11194918
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-00864-1
β-hydroxybutyrate resensitizes colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by suppressing H3K79 methylation in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Ketone β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) has been reported to prevent tumor cell proliferation and improve drug resistance. However, the effectiveness of BHB in oxaliplatin (Oxa)-resistant colorectal cancer (CRC) and the underlying mechanism still require further proof.
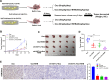
Methods: CRC-Oxa-resistant strains were established by increasing concentrations of CRC cells to Oxa. CRC-Oxa cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) were checked following BHB intervention in vitro. The subcutaneous and metastasis models were established to assess the effects of BHB on the growth and metastasis of CRC-Oxa in vivo. Eight Oxa responders and seven nonresponders with CRC were enrolled in the study. Then, the serum BHB level and H3K79me, H3K27ac, H3K14ac, and H3K9me levels in tissues were detected. DOT1L (H3K79me methyltransferase) gene knockdown or GNE-049 (H3K27ac inhibitor) use was applied to analyze further whether BHB reversed CRC-Oxa resistance via H3K79 demethylation and/or H3K27 deacetylation in vivo and in vitro.
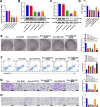
Results: Following BHB intervention based on Oxa, the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of CRC-Oxa cells and the growth and metastasis of transplanted tumors in mice were suppressed. Clinical analysis revealed that the differential change in BHB level was associated with drug resistance and was decreased in drug-resistant patient serum. The H3K79me, H3K27ac, and H3K14ac expressions in CRC were negatively correlated with BHB. Furthermore, results indicated that H3K79me inhibition may lead to BHB target deletion, resulting in its inability to function.
Conclusions: β-hydroxybutyrate resensitized CRC cells to Oxa by suppressing H3K79 methylation in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Drug resistance; H3K79me; Oxaliplatin; Β-hydroxybutyrate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

