Overcoming effector T cell exhaustion in ovarian cancer ascites with a novel adenovirus encoding for a MUC1 bispecific antibody engager and IL-2 cytokine
- PMID: 38910324
- PMCID: PMC11403222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.06.029
Overcoming effector T cell exhaustion in ovarian cancer ascites with a novel adenovirus encoding for a MUC1 bispecific antibody engager and IL-2 cytokine
Erratum in
-
Overcoming effector T cell exhaustion in ovarian cancer ascites with a novel adenovirus encoding for a MUC1 bispecific antibody engager and IL-2 cytokine.Mol Ther. 2024 Aug 7;32(8):2800. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.07.009. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39029457 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
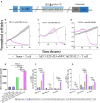
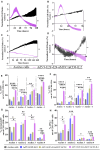
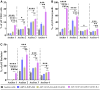
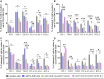
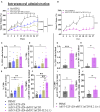
T cell-focused cancer immunotherapy including checkpoint inhibitors and cell therapies has been rapidly evolving over the past decade. Nevertheless, there remains a major unmet medical need in oncology generally and immuno-oncology specifically. We have constructed an oncolytic adenovirus, Ad5/3-E2F-d24-aMUC1aCD3-IL-2 (TILT-322), which is armed with a human aMUC1aCD3 T cell engager and IL-2. TILT-322 treatment stimulated T cell cytotoxicity through the increased presence of granzyme B, perforin, and interferon-gamma. Additional immune profiling indicated TILT-322 increased gamma delta T cell activation and impacted other cell types such as natural killer cells and natural killer-like T cells that are traditionally involved in cancer immunotherapy. TILT-322 treatment also decreased the proportion of exhausted CD8+ T cells as demarked by immune checkpoint expression in ovarian ascites samples. Overall, our data showed that TILT-322 treatment led to an enhanced T cell activation and reversed T cell exhaustion translating into high antitumor efficacy when given locally or intravenously. The analysis of blood and tumors isolated from an in vivo patient-derived ovarian cancer xenograft model suggested TILT-322 mediated tumor control through improved T cell functions. Therefore, TILT-322 is a promising novel anti-tumor agent for clinical translation.
Keywords: IL-2; Mucin1; T cell exhaustion; bispecific T cell engager; oncolytic adenovirus.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.H. is a shareholder of Circio Holdings ASA. (Norway). A.H., J.C., J.M.S., and D.Q. are employees and shareholders of TILT Biotherapeutics, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Havunen R., Siurala M., Sorsa S., Grönberg-Vähä-Koskela S., Behr M., Tähtinen S., Santos J.M., Karell P., Rusanen J., Nettelbeck D.M., et al. Oncolytic Adenoviruses Armed with Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Interleukin-2 Enable Successful Adoptive Cell Therapy. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2017;4:77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2016.12.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liikanen I., Basnet S., Quixabeira D.C.A., Taipale K., Hemminki O., Oksanen M., Kankainen M., Juhila J., Kanerva A., Joensuu T., et al. Oncolytic adenovirus decreases the proportion of TIM-3 + subset of tumor-infiltrating CD8 + T cells with correlation to improved survival in patients with cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2022;10:e003490. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003490. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basnet S., Santos J.M., Quixabeira D.C.A., Clubb J.H.A., Grönberg-Vähä-Koskela S.A.M., Arias V., Pakola S., Kudling T.V., Heiniö C., Havunen R., et al. Oncolytic adenovirus coding for bispecific T cell engager against human MUC-1 potentiates T cell response against solid tumors. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2023;28:59–73. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.12.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

