Piloting the adaptation of the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children-2 nd edition (KABC-II) to assess school-age neurodevelopment in rural Zimbabwe
- PMID: 38910935
- PMCID: PMC11190652
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.17902.2
Piloting the adaptation of the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children-2 nd edition (KABC-II) to assess school-age neurodevelopment in rural Zimbabwe
Abstract
Background: Neurodevelopment assessment tools for low-resource settings are urgently needed. However, most available tools were developed in high-income settings and may lack cross-cultural validity.
Methods: We piloted and adapted two subtests within the planning domain of the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children-2nd edition (KABC-II) for use in rural Zimbabwean children aged 7years. After initial assessments of face validity, we created 4 substitutions for the story completion subtest and 7 additions for the pattern reasoning subtest through a co-design process with fieldworkers and child development experts. To assess how successful the changes were, T-tests adjusting for unequal variances were used to compare scores between the original and adapted versions of the same subtest. ANOVA and pairwise analysis was performed to compare the performance of KABC-II subtests across domains. Intraclass correlation coefficient was calculated to explore the variability between domains.
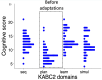
Results: Initial test scores on the planning domain were significantly lower than the other three domains of learning, sequential memory and simultaneous reasoning (P<0.001) in 50 children (mean age 7.6(SD 0.2) years). Modified subtests were administered to another 20 children (mean age 7.6(SD 0.2) years), who showed story completion scores that were 0.7 marks higher (95% CI 0.0, 1.4; P=0.05) and pattern reasoning scores 1.8 marks higher (95% CI 0.5, 3.2; P=0.01). Overall, the planning domain mean score increased from 8.1 (SD 2.9) to 10.6 (SD 3.4). The intra class correlation coefficient between all four KABC-II domains was initially 0.43 (95% CI 0.13, 0.64) and after modification was 0.69 (95% CI 0.37, 0.87), suggesting an increase in the construct validity.
Conclusions: The KABC-II planning domain was successfully adapted to improve cross-cultural validity. Construct validity was enhanced, based on increased inter-correlations among scales. The process of co-design to modify tests for new settings may be beneficial for other commonly used neurodevelopmental tools.
Keywords: Child development; School-age; Sub-Saharan Africa; cognition.
Copyright: © 2024 Piper JD et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Wechsler D: Wechsler intelligence scale for children.Pearson; 2014. Reference Source
-
- Bayley N: Bayley scales of infant and toddler development.Pearson; 2005. Reference Source
-
- Kaufmann A, Kaufmann N: Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children 2nd edition.In: PsychCorp. ed.: Pearson; 2004.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

