Incidence of Mortality and Its Relation to Comorbidity in Ludwig's Angina: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38911416
- PMCID: PMC11189848
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-024-02116-5
Incidence of Mortality and Its Relation to Comorbidity in Ludwig's Angina: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
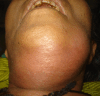
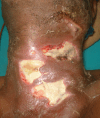
Introduction: Ludwig's angina is a serious life-threatening infective condition of maxillofacial region due to odontogenic origin which is clinically diagnosed by its clinical signs and symptoms. Airway management and early surgical decompression is the main stay of management. The mortality rates in Ludwig's angina remains multivariate. There is a paucity in literature regarding the mortality rates of this disease.
Aim and objectives: Aim of this retrospective study is to describes the characteristics, probable cause of death and mortality rates of patients with co-morbidities presenting to the emergency department (ED) who were subsequently admitted with a primary diagnosis of Ludwig's angina.
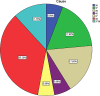
Materials and method: Study was conducted in the department of maxillofacial surgery in a tertiary care teaching hospital from Jan 2011 to Dec 2022. Data of 17 patients who were clinically diagnosed as Ludwig's angina were included in the study. The comorbidity, source of odontongenic cause, mode of intubation and the outcome of the disease were evaluated.
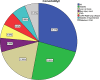
Result: Comparison of categorical variables was done using Fishers exact test. A p-value of <0.7 was considered statistically significant. The results suggested that Out of 17 patients 12 patients (70.5%), 7 male and 5 females had comorbidities and four cases (23.5%) had complication of death, all having co-morbidities.
Summary: It concludes that associated comorbidity has a significant role in progress and outcome of the disease and incidence of death is more common in cases having associated comorbidity.
Keywords: Airway management; Comorbidity; Infected mandibular molars; Ludwig’s angina; Mortality rate.
© The Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fritsch DE, Klein DG. Ludwig's angina. Heart Lung. 1992;21(1):39–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials