The SAEORA Flap for Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction: A Novel Flap Design without the Use of Acellular Dermal Matrices
- PMID: 38911580
- PMCID: PMC11191962
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005852
The SAEORA Flap for Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction: A Novel Flap Design without the Use of Acellular Dermal Matrices
Abstract
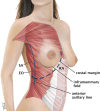
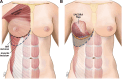
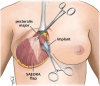
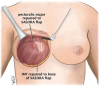
Background: The gold standard for implant-based breast reconstruction uses acellular dermal matrices (ADMs). They provide improved inferolateral pole coverage, reduced capsular contracture rates, and increased primary expander fill volumes. However, ADMs are costly and have been associated with increased rates of postoperative infection, seroma, hematoma, implant malposition, and mastectomy flap necrosis (MFN). This study describes a novel autologous flap without the need of ADM, the serratus anterior external oblique rectus abdominis (SAEORA) flap, as an alternative in prosthetic-based breast reconstruction.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on all patients who underwent SAEORA flap breast reconstruction by a single surgeon between January 1, 2013 and May 31, 2020 at a single institution. Patient demographics, diagnosis, treatment, tissue expander (TE) volume, implant size, complications, and results were assessed.
Results: Forty-seven patients underwent 78 SAEORA flaps. Sixty-two had TEs placed, and 14 were direct-to-implant. Mean body mass index was 23.1 kg per m². Median primary TE fill volume was 150 mL, and final implant volume average was 450 mL. Mean follow-up was 14.5 months. Complications included infection/cellulitis (7.9%), seroma (6.6%), hematoma (5.2%), and MFN (7.9%).
Conclusions: The SAEORA flap is a novel autologous flap and is a viable option for prosthetic-based breast reconstruction, with an acceptable complication profile relative to ADM-based reconstructions. Additionally, SAEORA is MFN-resistant and has been used effectively in salvage of exposed implants or ADM, and in double-bubble deformity correction.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures
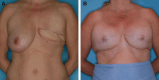
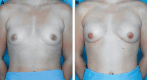
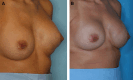
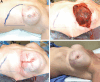
Similar articles
-
Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction with Fenestrated Acellular Dermal Matrix: A Novel Design.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018 Apr 4;6(4):e1712. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001712. eCollection 2018 Apr. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018. PMID: 29876165 Free PMC article.
-
Cost analysis of postmastectomy reconstruction: A comparison of two staged implant reconstruction using tissue expander and acellular dermal matrix with abdominal-based perforator free flaps.J Surg Oncol. 2017 Sep;116(4):439-447. doi: 10.1002/jso.24692. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28591940
-
The Effect of Sterile Acellular Dermal Matrix Use on Complication Rates in Implant-Based Immediate Breast Reconstructions.Arch Plast Surg. 2016 Nov;43(6):523-528. doi: 10.5999/aps.2016.43.6.523. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Arch Plast Surg. 2016. PMID: 27896182 Free PMC article.
-
Alloplastic adjuncts in breast reconstruction.Gland Surg. 2016 Apr;5(2):158-73. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.06.02. Gland Surg. 2016. PMID: 27047784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focus on technique: supporting the soft-tissue envelope in breast reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012 Nov;130(5 Suppl 2):89S-94S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182625852. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012. PMID: 23096992 Review.
References
-
- Chen Z, Xu L, Shi W, et al. . Trends of female and male breast cancer incidence at the global, regional, and national levels, 1990–2017. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020;180:481–490. - PubMed
-
- Cemal Y, Albornoz CR, Disa JJ, et al. . A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: part 2. The influence of changing mastectomy patterns on reconstructive rate and method. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:320e–326e. - PubMed
-
- Albornoz CR, Bach PB, Mehrara BJ, et al. . A paradigm shift in U.S. Breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:15–23. - PubMed
-
- De Blacam C, Momoh AO, Colakoglu S, et al. . Cost analysis of implant-based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix. Ann Plast Surg. 2012;69:516–520. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
