New Pyrimidinone Bearing Aminomethylenes and Schiff Bases as Potent Antioxidant, Antibacterial, SARS-CoV-2, and COVID-19 Main Protease MPro Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Bioactivities, and Computational Studies
- PMID: 38911743
- PMCID: PMC11191110
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09393
New Pyrimidinone Bearing Aminomethylenes and Schiff Bases as Potent Antioxidant, Antibacterial, SARS-CoV-2, and COVID-19 Main Protease MPro Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Bioactivities, and Computational Studies
Abstract
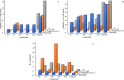
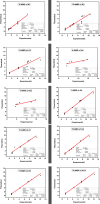
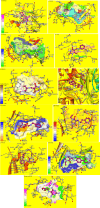
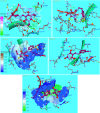
New 2-thioxopyrimidinone derivatives (A1-A10) were synthesized in 87-96% yields via a simple three-component condensation reaction. These compounds were screened extensively through in vitro assays for antioxidant and antibacterial investigations. The DPPH assays resulted in the excellent potency of A6-A10 as antioxidants with IC50 values of 0.83 ± 0.125, 0.90 ± 0.77, 0.36 ± 0.063, 1.4 ± 0.07, and 1.18 ± 0.06 mg/mL, which were much better than 1.79 ± 0.045 mg/mL for the reference ascorbic acid. These compounds exhibited better antibacterial potency against Klebsiella with IC50 values of 2 ± 7, 1.32 ± 8.9, 1.19 ± 11, 1.1 ± 12, and 1.16 ± 11 mg/mL for A6-A10. High-throughput screenings (HTS) of these motifs were carried out including investigation of drug-like behaviors, physiochemical property evaluation, and structure-related studies involving DFT and metabolic transformation trends. The radical scavenging ability of the synthesized motifs was validated through molecular docking studies through ligand-protein binding against human inducible nitric oxide synthase (HINOS) PDB ID: 4NOS, and the results were promising. Furthermore, the antiviral capability of the compounds was examined by in silico studies using two viral proteins PDB ID: 6Y84 and PDB ID: 6LU7. Binding poses of ligands were discussed, and amino acids in the protein binding pockets were investigated, where the tested compounds showed much better binding affinities than the standard inhibitors, proving to be suitable leads for antiviral drug discovery. The stabilities of the molecular docked complexes in real systems were validated by molecular dynamics simulations.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








References
-
- Tylińska B.; Wiatrak B.; Czyżnikowska Ż.; Cieśla-Niechwiadowicz A.; Gębarowska E.; Janicka-Kłos A. Novel pyrimidine derivatives as potential anticancer agents: Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking study. Int. j. mol. sci. 2021, 22 (8), 3825.10.3390/ijms22083825. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
