Reappraising the Role of T Cell-Derived IFN-γ in Restriction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the Murine Lung
- PMID: 38912839
- PMCID: PMC11249196
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2400145
Reappraising the Role of T Cell-Derived IFN-γ in Restriction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the Murine Lung
Abstract
T cells producing IFN-γ have long been considered a stalwart for immune protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), but their relative importance to pulmonary immunity has been challenged by murine studies that achieved protection by adoptively transferred Mtb-specific IFN-γ-/- T cells. Using IFN-γ-/- T cell chimeric mice and adoptive transfer of IFN-γ-/- T cells into TCRβ-/-δ-/- mice, we demonstrate that control of lung Mtb burden is in fact dependent on T cell-derived IFN-γ, and, furthermore, mice selectively deficient in T cell-derived IFN-γ develop exacerbated disease compared with T cell-deficient control animals, despite equivalent lung bacterial burdens. Deficiency in T cell-derived IFN-γ skews infected and bystander monocyte-derived macrophages to an alternative M2 phenotype and promotes neutrophil and eosinophil influx. Our studies support an important role for T cell-derived IFN-γ in pulmonary immunity against tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2024 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

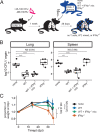
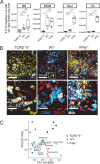
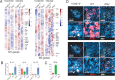
Update of
-
Re-appraising the role of T-cell derived interferon gamma in restriction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the murine lung: T-cell derived IFNγ is required to restrict pulmonary Mtb.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 5:2024.04.04.588086. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.04.588086. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Immunol. 2024 Aug 1;213(3):339-346. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2400145. PMID: 38617280 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Caruso, A. M., Serbina N., Klein E., Triebold K., Bloom B. R., Flynn J. L.. 1999. Mice deficient in CD4 T cells have only transiently diminished levels of IFN-gamma, yet succumb to tuberculosis. J. Immunol. 162: 5407–5416. - PubMed
-
- Casanova, J.-L., Abel L.. 2002. Genetic dissection of immunity to mycobacteria: the human model. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20: 581–620. - PubMed
-
- Esmail, H., Riou C., Du Bruyn E., Lai R. P.-J., Harley Y. X. R., Meintjes G., Wilkinson K. A., Wilkinson R. J.. 2018. The immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in HIV-1-coinfected persons. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 36: 603–638. - PubMed
-
- Pearl, J. E., Saunders B., Ehlers S., Orme I. M., Cooper A. M.. 2001. Inflammation and lymphocyte activation during mycobacterial infection in the interferon-γ-deficient mouse. Cell. Immunol. 211: 43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

