Safety and pharmacokinetics of VRC07-523LS administered via different routes and doses (HVTN 127/HPTN 087): A Phase I randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38913710
- PMCID: PMC11251612
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004329
Safety and pharmacokinetics of VRC07-523LS administered via different routes and doses (HVTN 127/HPTN 087): A Phase I randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) are a promising approach for HIV-1 prevention. In the Antibody Mediated Prevention (AMP) trials, a CD4-binding site targeting bnAb, VRC01, administered intravenously (IV), demonstrated 75% prevention efficacy against highly neutralization-sensitive viruses but was ineffective against less sensitive viruses. VRC07-523LS is a next-generation bnAb targeting the CD4-binding site and was engineered for increased neutralization breadth and half-life. We conducted a multicenter, randomized, partially blinded Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety and serum concentrations of VRC07-523LS, administered in multiple doses and routes to healthy adults without HIV.
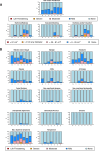
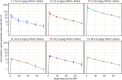
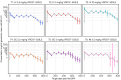
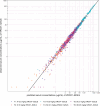
Methods and findings: Participants were recruited between 2 February 2018 and 9 October 2018. A total of 124 participants were randomized to receive 5 VRC07-523LS administrations via IV (T1: 2.5 mg/kg, T2: 5 mg/kg, T3: 20 mg/kg), subcutaneous (SC) (T4: 2.5 mg/kg, T5: 5 mg/kg), or intramuscular (IM) (T6: 2.5 mg/kg or P6: placebo) routes at 4-month intervals. Participants and site staff were blinded to VRC07-523LS versus placebo for the IM group, while all other doses and routes were open-label. Safety data were collected for 144 weeks following the first administration. VRC07-523LS serum concentrations were measured by ELISA through Day 112 in all participants and by binding antibody multiplex assay (BAMA) thereafter in 60 participants (10 per treatment group) through Day 784. Compartmental population pharmacokinetic (PK) analyses were conducted to evaluate the VRC07-523LS serum PK. Neutralization activity was measured in a TZM-bl assay and antidrug antibodies (ADAs) were assayed using a tiered bridging assay testing strategy. Injections and infusions were well tolerated, with mild pain or tenderness reported commonly in the SC and IM groups, and mild to moderate erythema or induration reported commonly in the SC groups. Infusion reactions were reported in 3 of 20 participants in the 20 mg/kg IV group. Peak geometric mean (GM) concentrations (95% confidence intervals [95% CIs]) following the first administration were 29.0 μg/mL (25.2, 33.4), 58.5 μg/mL (49.4, 69.3), and 257.2 μg/mL (127.5, 518.9) in T1-T3 with IV dosing; 10.8 μg/mL (8.8, 13.3) and 22.8 μg/mL (20.1, 25.9) in T4-T5 with SC dosing; and 16.4 μg/mL (14.7, 18.2) in T6 with IM dosing. Trough GM (95% CIs) concentrations immediately prior to the second administration were 3.4 μg/mL (2.5, 4.6), 6.5 μg/mL (5.6, 7.5), and 27.2 μg/mL (23.9, 31.0) with IV dosing; 0.97 μg/mL (0.65, 1.4) and 3.1 μg/mL (2.2, 4.3) with SC dosing, and 2.6 μg/mL (2.05, 3.31) with IM dosing. Peak VRC07-523LS serum concentrations increased linearly with the administered dose. At a given dose, peak and trough concentrations, as well as serum neutralization titers, were highest in the IV groups, reflecting the lower bioavailability following SC and IM administration. A single participant was found to have low titer ADA at a lone time point. VRC07-523LS has an estimated mean half-life of 42 days across all doses and routes (95% CI: 40.5, 43.5), over twice as long as VRC01 (15 days).
Conclusions: VRC07-523LS was safe and well tolerated across a range of doses and routes and is a promising long-acting bnAb for inclusion in HIV-1 prevention regimens.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov/ NCT03387150 (posted on 21 December 2017).
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
SRW has conducted clinical trials funded by Janssen Vaccines, Moderna, Pfizer, Vir, Worcester HIV Vaccine, and Sanofi Pasteur, and serves on Independent Data Monitoring Committees for Janssen Vaccines and BioNTech; SRW’s spouse is an employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and may hold stock and/or stock options. CLG has received research support from Gilead and ViiV Healthcare and conducted clinical trials funded by Moderna and Novavax. MEA has received research support from Janssen, Be Bio, and Moderna.
Figures



Update of
-
A Randomised Clinical Trial of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of VRC07-523LS Administered via Different Routes and Doses (HVTN 127/HPTN 087).medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 11:2024.01.10.23299799. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.10.23299799. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Med. 2024 Jun 24;21(6):e1004329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004329. PMID: 38260276 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS statistics—Fact sheet. 2023. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004406/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068614/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068618/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068614/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

