The neuron as a direct data-driven controller
- PMID: 38913890
- PMCID: PMC11228465
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311893121
The neuron as a direct data-driven controller
Abstract
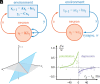
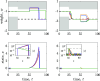
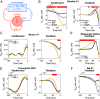
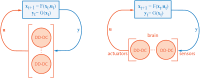
In the quest to model neuronal function amid gaps in physiological data, a promising strategy is to develop a normative theory that interprets neuronal physiology as optimizing a computational objective. This study extends current normative models, which primarily optimize prediction, by conceptualizing neurons as optimal feedback controllers. We posit that neurons, especially those beyond early sensory areas, steer their environment toward a specific desired state through their output. This environment comprises both synaptically interlinked neurons and external motor sensory feedback loops, enabling neurons to evaluate the effectiveness of their control via synaptic feedback. To model neurons as biologically feasible controllers which implicitly identify loop dynamics, infer latent states, and optimize control we utilize the contemporary direct data-driven control (DD-DC) framework. Our DD-DC neuron model explains various neurophysiological phenomena: the shift from potentiation to depression in spike-timing-dependent plasticity with its asymmetry, the duration and adaptive nature of feedforward and feedback neuronal filters, the imprecision in spike generation under constant stimulation, and the characteristic operational variability and noise in the brain. Our model presents a significant departure from the traditional, feedforward, instant-response McCulloch-Pitts-Rosenblatt neuron, offering a modern, biologically informed fundamental unit for constructing neural networks.
Keywords: control; dynamics; neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barlow H., Redundancy reduction revisited. Network 12, 241 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan M. V., Laughlin S. B., Dubs A., Predictive coding: A fresh view of inhibition in the retina. Proc. R. Soc. London B 216, 427–459 (1982). - PubMed
-
- Atick J. J., Could information theory provide an ecological theory of sensory processing? Network 3, 213–251 (1992). - PubMed
-
- van Hateren J. H., Theoretical predictions of spatiotemporal receptive fields of fly LMCS, and experimental validation. J. Comp. Physiol. A 171, 157–170 (1992).
-
- Simoncelli E. P., Olshausen B. A., Natural image statistics and neural representation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 1193–1216 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

