Associations of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor with organ dysfunctions in septic shock
- PMID: 38914630
- PMCID: PMC11196691
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65262-3
Associations of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor with organ dysfunctions in septic shock
Abstract
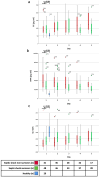
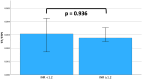
Coagulopathy, microvascular alterations and concomitant organ dysfunctions are hallmarks of sepsis. Attempts to attenuate coagulation activation with an inhibitor of tissue factor (TF), i.e. tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), revealed no survival benefit in a heterogenous group of sepsis patients, but a potential survival benefit in patients with an international normalized ratio (INR) < 1.2. Since an increased TF/TFPI ratio determines the procoagulant activity specifically on microvascular endothelial cells in vitro, we investigated whether TF/TFPI ratio in blood is associated with INR alterations, organ dysfunctions, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and outcome in septic shock. Twenty-nine healthy controls (HC) and 89 patients with septic shock admitted to a tertiary ICU were analyzed. TF and TFPI in blood was analyzed and related to organ dysfunctions, DIC and mortality. Patients with septic shock had 1.6-fold higher levels of TF and 2.9-fold higher levels of TFPI than HC. TF/TFPI ratio was lower in septic shock compared to HC (0.003 (0.002-0.005) vs. 0.006 (0.005-0.008), p < 0.001). Non-survivors had higher TFPI levels compared to survivors (43038 (29354-54023) vs. 28041 (21675-46582) pg/ml, p = 0.011). High TFPI levels were associated with acute kidney injury, liver dysfunction, DIC and disease severity. There was a positive association between TF/TFPI ratio and troponin T (b = 0.531 (0.309-0.754), p < 0.001). A high TF/TFPI ratio is exclusively associated with myocardial injury but not with other organ dysfunctions. Systemic TFPI levels seem to reflect disease severity. These findings point towards a pathophysiologic role of TF/TFPI in sepsis-induced myocardial injury.
Keywords: Coagulation; Microvasculature; Sepsis; Septic shock; Tissue factor; Tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham E, Reinhart K, Svoboda P, Seibert A, Olthoff D, Dal Nogare A, et al. Assessment of the safety of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with severe sepsis: A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind, dose escalation study. Crit. Care Med. 2001;29(11):2081–2089. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200111000-00007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

