Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccinations for adults: systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials
- PMID: 38915011
- PMCID: PMC11197367
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03471-3
Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccinations for adults: systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials
Abstract
Background: To combat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), booster vaccination strategies are important. However, the optimal administration of booster vaccine platforms remains unclear. Herein, we aimed to assess the benefits and harms of three or four heterologous versus homologous booster regimens.
Methods: From November 3 2022 to December 21, 2023, we searched five databases for randomised clinical trials (RCT). Reviewers screened, extracted data, and assessed bias risks independently with the Cochrane risk-of-bias 2 tool. We conducted meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses (TSA) on our primary (all-cause mortality; laboratory confirmed symptomatic and severe COVID-19; serious adverse events [SAE]) and secondary outcomes (quality of life [QoL]; adverse events [AE] considered non-serious). We assessed the evidence with the GRADE approach. Subgroup analyses were stratified for trials before and after 2023, three or four boosters, immunocompromised status, follow-up, risk of bias, heterologous booster vaccine platforms, and valency of booster.
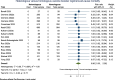
Results: We included 29 RCTs with 43 comparisons (12,538 participants). Heterologous booster regimens may not reduce the relative risk (RR) of all-cause mortality (11 trials; RR 0.86; 95% CI 0.33 to 2.26; I2 0%; very low certainty evidence); laboratory-confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 (14 trials; RR 0.95; 95% CI 0.72 to 1.25; I2 0%; very low certainty); or severe COVID-19 (10 trials; RR 0.51; 95% CI 0.20 to 1.33; I2 0%; very low certainty). For safety outcomes, heterologous booster regimens may have no effect on SAE (27 trials; RR 1.15; 95% CI 0.68 to 1.95; I2 0%; very low certainty) but may raise AE considered non-serious (20 trials; RR 1.19; 95% CI 1.08 to 1.32; I2 64.4%; very low certainty). No data on QoL was available. Our TSAs showed that the cumulative Z curves did not reach futility for any outcome.
Conclusions: With our current sample sizes, we were not able to infer differences of effects for any outcomes, but heterologous booster regimens seem to cause more non-serious AE. Furthermore, more robust data are instrumental to update this review.
Keywords: Booster immunisation; COVID-19 vaccines; Heterologous immunity; Homologous immunity; Vaccine efficacy; Vaccine safety.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SM received consulting fees as a consultant for the P-95 consulting firm. ART reports leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group, unpaid with the Danish Society of Immunology as chairman. AS reports leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group, unpaid with Cochrane as a steering member of the Cochrane Early Career Professionals Network. All other authors declared no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- WHO. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update - Edition 158. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
-
- WHO. Global COVID-19 vaccination strategy in a changing world. July 2022 Update. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/global-covid-19-vaccination-stra....
-
- WHO. SAGE updates COVID-19 vaccination guidance. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-03-2023-sage-updates-covid-19-vaccinati....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

