This is a preprint.
Cholesterol inhibits assembly and activation of the EphA2 receptor
- PMID: 38915729
- PMCID: PMC11195142
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.10.598255
Cholesterol inhibits assembly and activation of the EphA2 receptor
Update in
-
Cholesterol inhibits assembly and oncogenic activation of the EphA2 receptor.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 11;8(1):411. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07786-6. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40069393 Free PMC article.
Abstract
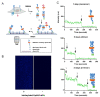
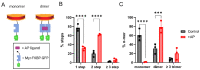
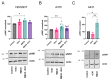
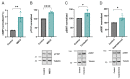
The receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 drives cancer malignancy by facilitating metastasis. EphA2 can be found in different self-assembly states: as a monomer, dimer, and oligomer. However, our understanding remains limited regarding which EphA2 state is responsible for driving pro-metastatic signaling. To address this limitation, we have developed SiMPull-POP, a single-molecule method for accurate quantification of membrane protein self-assembly. Our experiments revealed that a reduction of plasma membrane cholesterol strongly promoted EphA2 self-assembly. Indeed, low cholesterol caused a similar effect to the EphA2 ligand ephrinA1-Fc. These results indicate that cholesterol inhibits EphA2 assembly. Phosphorylation studies in different cell lines revealed that low cholesterol increased phospho-serine levels, the signature of oncogenic signaling. Investigation of the mechanism that cholesterol uses to inhibit the assembly and activity of EphA2 indicate an in-trans effect, where EphA2 is phosphorylated by protein kinase A downstream of beta-adrenergic receptor activity, which cholesterol also inhibits. Our study not only provides new mechanistic insights on EphA2 oncogenic function, but also suggests that cholesterol acts as a molecular safeguard mechanism that prevents uncontrolled self-assembly and activation of EphA2.
Figures

References
-
- Pasquale E. B. Eph-Ephrin Bidirectional Signaling in Physiology and Disease. Cell 133, 38–52 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Boyd A. W., Bartlett P. F. & Lackmann M. Therapeutic targeting of EPH receptors and their ligands. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 13, 39–62 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Kania A. & Klein R. Mechanisms of ephrin-Eph signalling in development, physiology and disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 17, 240–256 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Thaker P. H. et al. EphA2 expression is associated with aggressive features in ovarian carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research 10, 5145–5150 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
