α-Synuclein Oligomers Displace Monomeric α-Synuclein from Lipid Membranes
- PMID: 38916260
- PMCID: PMC11238581
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c10889
α-Synuclein Oligomers Displace Monomeric α-Synuclein from Lipid Membranes
Abstract
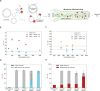
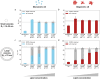
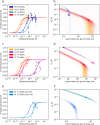
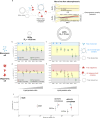
Parkinson's disease (PD) is an increasingly prevalent and currently incurable neurodegenerative disorder linked to the accumulation of α-synuclein (αS) protein aggregates in the nervous system. While αS binding to membranes in its monomeric state is correlated to its physiological role, αS oligomerization and subsequent aberrant interactions with lipid bilayers have emerged as key steps in PD-associated neurotoxicity. However, little is known of the mechanisms that govern the interactions of oligomeric αS (OαS) with lipid membranes and the factors that modulate such interactions. This is in large part due to experimental challenges underlying studies of OαS-membrane interactions due to their dynamic and transient nature. Here, we address this challenge by using a suite of microfluidics-based assays that enable in-solution quantification of OαS-membrane interactions. We find that OαS bind more strongly to highly curved, rather than flat, lipid membranes. By comparing the membrane-binding properties of OαS and monomeric αS (MαS), we further demonstrate that OαS bind to membranes with up to 150-fold higher affinity than their monomeric counterparts. Moreover, OαS compete with and displace bound MαS from the membrane surface, suggesting that disruption to the functional binding of MαS to membranes may provide an additional toxicity mechanism in PD. These findings present a binding mechanism of oligomers to model membranes, which can potentially be targeted to inhibit the progression of PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; aggregation; lipids; membranes; oligomers; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Magdalena A. Czekalska, Quentin Peter, and Thomas Mueller are former employees of Fluidic Analytics Ltd., which is developing and commercializing microfluidic diffusional sizing and electrophoresis instrumentation. Sebastian Fiedler and Sean R. A. Devenish were employees of Fluidic Analytics Ltd. Tuomas P. J. Knowles was a founder and a member of the board of directors of Fluidic Analytics Ltd. Catherine K. Xu was a consultant for Fluidic Analytics Ltd. Greta Sneideriene received funding from Fluidic Analytics Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Froula J. M.; Castellana-Cruz M.; Anabtawi N. M.; Camino J. D.; Chen S. W.; Thrasher D. R.; Freire J.; Yazdi A. A.; Fleming S.; Dobson C. M.; Kumita J. R.; Cremades N.; Volpicelli-Daley L. A. Defining Alpha-Synuclein Species Responsible for Parkinson’s Disease Phenotypes in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10392–10406. 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fortuna J. T. S.; Gralle M.; Beckman D.; Neves F. S.; Diniz L. P.; Frost P. S.; Barros-Aragão F.; Santos L. E.; Gonçalves R. A.; Romão L.; Zamberlan D. C.; Soares F. A. A.; Braga C.; Foguel D.; Gomes F. C. A.; Felice F. G.; De Ferreira S. T.; Clarke J. R.; Figueiredo C. P. Brain Infusion of Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Induces Motor and Non-Motor Parkinson’s Disease-like Symptoms in Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 333, 150–160. 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.06.047. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

