TGFβ in Pancreas and Colorectal Cancer: Opportunities to Overcome Therapeutic Resistance
- PMID: 38916900
- PMCID: PMC11371528
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0468
TGFβ in Pancreas and Colorectal Cancer: Opportunities to Overcome Therapeutic Resistance
Abstract
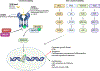
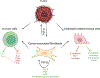
TGFβ is a pleiotropic signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in regulating a multitude of cellular functions. TGFβ has a dual role in cell regulation where it induces growth inhibition and cell death; however, it can switch to a growth-promoting state under cancerous conditions. TGFβ is upregulated in colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer, altering the tumor microenvironment and immune system and promoting a mesenchymal state. The upregulation of TGFβ in certain cancers leads to resistance to immunotherapy, and attempts to inhibit TGFβ expression have led to reduced therapeutic resistance when combined with chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Here, we review the current TGFβ inhibitor drugs in clinical trials for pancreatic and colorectal cancer, with the goal of uncovering advances in improving clinical efficacy for TGFβ combinational treatments in patients. Furthermore, we discuss the relevance of alterations in TGFβ signaling and germline variants in the context of personalizing treatment for patients who show lack of response to current therapeutics.
©2024 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforming Growth Factor β Mediates Drug Resistance by Regulating the Expression of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 in Colorectal Cancer.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 12;291(33):17405-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.713735. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2016. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4368. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W120.013237. PMID: 27330076 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta signaling reduces pancreatic adenocarcinoma growth and invasiveness.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;72(1):152-61. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.029025. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17400764
-
Transforming Growth Factor-β Blockade in Pancreatic Cancer Enhances Sensitivity to Combination Chemotherapy.Gastroenterology. 2023 Oct;165(4):874-890.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.038. Epub 2023 May 30. Gastroenterology. 2023. PMID: 37263309 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting transforming growth factor-β signaling for enhanced cancer chemotherapy.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(3):1345-1363. doi: 10.7150/thno.51383. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGFβ and the Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer.Cells. 2023 Apr 12;12(8):1139. doi: 10.3390/cells12081139. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PDCD10 promotes the tumor-supporting functions of TGF-β in pancreatic cancer.Clin Sci (Lond). 2024 Sep 18;138(18):1111-1129. doi: 10.1042/CS20240450. Clin Sci (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39212293 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 12;26(12):5635. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125635. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic profiling identifies a stromal TGF-β1/podoplanin axis as a driver of colorectal cancer progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 22;44(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03496-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40842027 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM channels in human cancers: regulatory mechanism and therapeutic prospects.Biomark Res. 2024 Dec 4;12(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00699-2. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39633507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical