Brain repair mechanisms after cell therapy for stroke
- PMID: 38916992
- PMCID: PMC11449145
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awae204
Brain repair mechanisms after cell therapy for stroke
Abstract
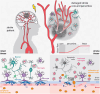
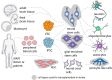
Cell-based therapies hold great promise for brain repair after stroke. While accumulating evidence confirms the preclinical and clinical benefits of cell therapies, the underlying mechanisms by which they promote brain repair remain unclear. Here, we briefly review endogenous mechanisms of brain repair after ischaemic stroke and then focus on how different stem and progenitor cell sources can promote brain repair. Specifically, we examine how transplanted cell grafts contribute to improved functional recovery either through direct cell replacement or by stimulating endogenous repair pathways. Additionally, we discuss recently implemented preclinical refinement methods, such as preconditioning, microcarriers, genetic safety switches and universal (immune evasive) cell transplants, as well as the therapeutic potential of these pharmacologic and genetic manipulations to further enhance the efficacy and safety of cell therapies. By gaining a deeper understanding of post-ischaemic repair mechanisms, prospective clinical trials may be further refined to advance post-stroke cell therapy to the clinic.
Keywords: brain injury; iPSC; ischaemia; regeneration; stem cells; therapy.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
L.L. is coinventor on the International Patent WO/2020/226993 filed in April 2020; the patent relates to the use of antibodies which specifically bind interleukin-1a to reduce various sequelae of ischemia-reperfusion injury to the central nervous system.
Figures

References
-
- Pu L, Wang L, Zhang R, Zhao T, Jiang Y, Han L. Projected global trends in ischemic stroke incidence, deaths and disability-adjusted life years from 2020 to 2030. Stroke. 2023;54:1330–1339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

