SUMO protease and proteasome recruitment at the nuclear periphery differently affect replication dynamics at arrested forks
- PMID: 38917328
- PMCID: PMC11317160
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae526
SUMO protease and proteasome recruitment at the nuclear periphery differently affect replication dynamics at arrested forks
Abstract
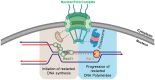
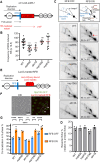
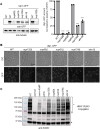
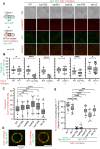
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) have emerged as genome organizers, defining a particular nuclear compartment enriched for SUMO protease and proteasome activities, and act as docking sites for the repair of DNA damage. In fission yeast, the anchorage of perturbed replication forks to NPCs is an integral part of the recombination-dependent replication restart mechanism (RDR) that resumes DNA synthesis at terminally dysfunctional forks. By mapping DNA polymerase usage, we report that SUMO protease Ulp1-associated NPCs ensure efficient initiation of restarted DNA synthesis, whereas proteasome-associated NPCs sustain the progression of restarted DNA polymerase. In contrast to Ulp1-dependent events, this last function is not alleviated by preventing SUMO chain formation. By analyzing the role of the nuclear basket, the nucleoplasmic extension of the NPC, we reveal that the activities of Ulp1 and the proteasome cannot compensate for each other and affect the dynamics of RDR in distinct ways. Our work probes two distinct mechanisms by which the NPC environment ensures optimal RDR, both controlled by different NPC components.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Berti M., Cortez D., Lopes M.. The plasticity of DNA replication forks in response to clinically relevant genotoxic stress. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020; 21:633–651. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty S., Schirmeisen K., Lambert S.A.. The multifaceted functions of homologous recombination in dealing with replication-associated DNA damages. DNA Repair (Amst.). 2023; 129:103548. - PubMed
-
- Carr A., Lambert S.. Recombination-dependent replication: new perspectives from site-specific fork barriers. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2021; 71:129–135. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

