Adaptive selection at G6PD and disparities in diabetes complications
- PMID: 38918629
- PMCID: PMC11555759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03089-1
Adaptive selection at G6PD and disparities in diabetes complications
Abstract
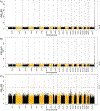
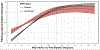
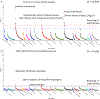
Diabetes complications occur at higher rates in individuals of African ancestry. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDdef), common in some African populations, confers malaria resistance, and reduces hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels by shortening erythrocyte lifespan. In a combined-ancestry genome-wide association study of diabetic retinopathy, we identified nine loci including a G6PDdef causal variant, rs1050828 -T (Val98Met), which was also associated with increased risk of other diabetes complications. The effect of rs1050828 -T on retinopathy was fully mediated by glucose levels. In the years preceding diabetes diagnosis and insulin prescription, glucose levels were significantly higher and HbA1c significantly lower in those with versus without G6PDdef. In the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial, participants with G6PDdef had significantly higher hazards of incident retinopathy and neuropathy. At the same HbA1c levels, G6PDdef participants in both ACCORD and the Million Veteran Program had significantly increased risk of retinopathy. We estimate that 12% and 9% of diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy cases, respectively, in participants of African ancestry are due to this exposure. Across continentally defined ancestral populations, the differences in frequency of rs1050828 -T and other G6PDdef alleles contribute to disparities in diabetes complications. Diabetes management guided by glucose or potentially genotype-adjusted HbA1c levels could lead to more timely diagnoses and appropriate intensification of therapy, decreasing the risk of diabetes complications in patients with G6PDdef alleles.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures
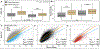
References
-
- Teo ZL, et al. Global Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy and Projection of Burden through 2045: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 128, 1580–1591 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K12 AR084232/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK120631/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 HL110380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY026877/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U18DP006711/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004406/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY025295/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- I01 CX001897/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- P30 EY025585/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY032159/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK127083/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U18 DP006711/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- I01 CX001481/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- F31EY033663/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- P30 EY011373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK120631/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY021453-10/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- F31 EY033663/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30EY026877/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R21AI156161/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
- R01AR074989/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
- T32 EY021453/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K12HD043483/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- TL1 TR002244/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL161516/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL161516/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- U01HG011723/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- U01 HG011723/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR074989/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001737/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- P30EY011373/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- UM1TR00406/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- UL1TR002378/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005233/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K12 HD043483/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004557/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- TL1TR002244/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- I01 BX005831/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY025295/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U18DP006711/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | CDC | National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (CDC's National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion)
- R01EY032159/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- P30EY025885/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R21 AI156161/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

