Skill development practice-related challenges, and associated factors among nursing students
- PMID: 38918751
- PMCID: PMC11197178
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-024-02115-4
Skill development practice-related challenges, and associated factors among nursing students
Abstract
Background: Nurse students reportedly face lots of challenges during skill development practice in health institutions. However, the prevalence of challenges and factors associated aren't well understood yet.
Objective: The objective of the study was to identify the challenges experienced by nursing students in health institutions during skill development practice.
Method: A cross-sectional study was employed on the participants selected using a simple random sampling technique. The data was cleaned using Epi-data and exported to SPSS for analysis. Logistic regression analysis and correlation analysis were carried out to identify the associated factors.
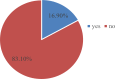
Result: The participants are more challenged by instructor factors (43.6%) and facility factors (40%). The prevalence of the challenge was 16.9%. Substance use and learning institutions are found to be independent predictors. A negative correlation was identified between the total challenge score and the overall competency score.
Conclusion: The determined nursing students' challenges are strong enough to affect the quality of education; therefore, it is essential to plan and improve the students' integrated supportive supervision.
Keywords: Associated factors; Challenges; Nursing student; Skill development practice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ibrahim A, Aly A. Clinical judgment among nursing interns. Clin Nurs Stud. 2018;6(3). 10.5430/cns.v6n3p19.
-
- Kim H, Suh EEJA. The effects of an interactive nursing skills mobile application on nursing students’ knowledge, self-efficacy, and skills performance: A randomized controlled trial. 2018;12(1):17–25. 10.1016/j.anr.2018.01.001. - PubMed
-
- Eyikara E, Baykara ZGJWJETCI. The importance of Simulation. Nurs Educ. 2017;9(1):2–7. doi: 10.18844/wjet.v9i1.543. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources