Liver Hemorrhage Following Mechanical CPR With the Lund University Cardiopulmonary Assist System (LUCAS) Device: A Focused Case Report
- PMID: 38919228
- PMCID: PMC11197923
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.61107
Liver Hemorrhage Following Mechanical CPR With the Lund University Cardiopulmonary Assist System (LUCAS) Device: A Focused Case Report
Abstract
Cardiac arrest is a leading cause of mortality globally, and mechanical CPR devices like the LUCAS system are designed to improve outcomes by enhancing consistency and reducing rescuer fatigue. However, this case report of a 76-year-old female who suffered cardiac arrest post-flight reveals significant complications associated with mechanical CPR. Despite achieving initial resuscitation, she developed extensive liver damage and additional complications, which ultimately led to her death. This case underscores the importance of precise training and strict adherence to guidelines when using mechanical CPR devices. It highlights that while these devices offer potential benefits, they also pose risks, especially for vulnerable patients, necessitating careful consideration and ongoing evaluation to optimize safety and effectiveness.
Keywords: cardiac arrest management; emergency resuscitation; liver damage; lucas device efficacy; massive pulmonary embolism; mechanical cpr; post-flight cardiac arrest.
Copyright © 2024, Harb et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
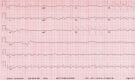
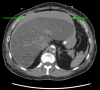
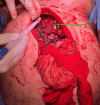
References
-
- American Heart Association. American Heart Association: CPR statistics. [ May; 2024 ]. 2021. https://cpr.heart.org/en/resources/cpr-facts-and-stats https://cpr.heart.org/en/resources/cpr-facts-and-stats
-
- Outcomes after mechanical versus manual chest compressions in eCPR patients. Gaisendrees C, Gerfer S, Ivanov B, et al. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2021;18:1023–1028. - PubMed
-
- Mechanical versus manual chest compression CPR under ground ambulance transport conditions. Fox J, Fiechter R, Gerstl P, et al. Acute Card Care. 2013;15:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
