The interplay between the microbiota and opioid in the treatment of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 38919504
- PMCID: PMC11197152
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1390046
The interplay between the microbiota and opioid in the treatment of neuropathic pain
Abstract
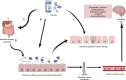
Neuropathic pain (NP) is characterized by its complex and multifactorial nature and limited responses to opioid therapy; NP is associated with risks of drug resistance, addiction, difficulty in treatment cessation, and psychological disorders. Emerging research on gut microbiota and their metabolites has demonstrated their effectiveness in alleviating NP and augmenting opioid-based pain management, concurrently mitigating the adverse effects of opioids. This review addresses the following key points: (1) the current advances in gut microbiota research and the challenges in using opioids to treat NP, (2) the reciprocal effects and benefits of gut microbiota on NP, and (3) the interaction between opioids with gut microbiota, as well as the benefits of gut microbiota in opioid-based treatment of NP. Through various intricate mechanisms, gut microbiota influences the onset and progression of NP, ultimately enhancing the efficacy of opioids in the management of NP. These insights pave the way for further pragmatic clinical research, ultimately enhancing the efficacy of opioid-based pain management.
Keywords: gut microbiota; gut-brain axis; neuropathic pain; opioids; pain.
Copyright © 2024 Gong, Xue, Luo, Yu, Hua and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gut microbiota regulates neuropathic pain: potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategy.J Headache Pain. 2020 Aug 17;21(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01170-x. J Headache Pain. 2020. PMID: 32807072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opioids and neuropathic pain.Pain Physician. 2012 Jul;15(3 Suppl):ES93-110. Pain Physician. 2012. PMID: 22786465 Review.
-
Integrated 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Metabolomics Analysis to Investigate the Important Role of Osthole on Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites in Neuropathic Pain Mice.Front Physiol. 2022 Feb 7;13:813626. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.813626. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35197864 Free PMC article.
-
The Gut-Brain Axis in Opioid Use Disorder: Exploring the Bidirectional Influence of Opioids and the Gut Microbiome-A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;14(10):1227. doi: 10.3390/life14101227. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota Modulation and Its Implications on Neuropathic Pain: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Pain Ther. 2024 Feb;13(1):33-51. doi: 10.1007/s40122-023-00565-3. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Pain Ther. 2024. PMID: 38087070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Bidirectional Interplay Between Substances of Abuse and Gut Microbiome Homeostasis.Life (Basel). 2025 May 22;15(6):834. doi: 10.3390/life15060834. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Ginger Root Extract on Pain Behaviors, Inflammation, and Mitochondrial Function in the Colon and Different Brain Regions of Male and Female Neuropathic Rats: A Gut-Brain Axis Study.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 21;16(20):3563. doi: 10.3390/nu16203563. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya C., Betrapally N. S., Gillevet P. M., Sterling R. K., Akbarali H., White M. B., et al. . (2017). Chronic opioid use is associated with altered gut microbiota and predicts readmissions in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 45, 319–331. doi: 10.1111/apt.13858, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

