T cell-related ubiquitination genes as prognostic indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38919610
- PMCID: PMC11196398
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424752
T cell-related ubiquitination genes as prognostic indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: T lymphocytes, integral to the adaptive immune system, wield pivotal influence in bolstering anti-tumor responses, and are strictly regulated by ubiquitination modification. The objective of this investigation was to devise a novel prognostic and immunotherapeutic efficacy predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma patients utilizing T cell-related ubiquitination genes (TCRUG).
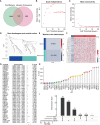
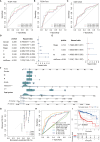
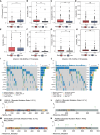
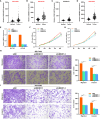
Method: The single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data and bulk RNA data of HCC patients are derived from the GEO database and TCGA database. Based on the processing of scRNA-seq, T cell marker genes are obtained and TCRUG is obtained. Further combined with WGCNA, differential analysis, univariate Cox regression analysis, LASSO analysis, and multivariate Cox regression analysis to filter and screen TCRUG. Finally construct a riskscore for predicting the prognosis of HCC patients, the predictive effect of which is validated in the GEO dataset. In addition, we also studied the correlation between riskscore and immunotherapy efficacy. Finally, the oncogenic role of UBE2E1 in HCC was explored through various in vitro experiments.
Result: Based on patients' scRNA-seq data, we finally obtained 3050 T cell marker genes. Combined with bulk RNA data and clinical data from the TCGA database, we constructed a riskscore that accurately predicts the prognosis of HCC patients. This riskscore is an independent prognostic factor for HCC and is used to construct a convenient column chart. In addition, we found that the high-risk group is more suitable for immunotherapy. Finally, the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of HCC cells significantly decreased after UBE2E1 expression reduction.
Conclusion: This study developed a riskscore based on TCRUG that can accurately and stably predict the prognosis of HCC patients. This riskscore is also effective in predicting the immune therapy response of HCC patients.
Keywords: HCC; T cell; UBE2E1; immunotherapy response; prognosis; ubiquitination modification.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Chen, Zhou, Ye, Xiong, Hu, Xu, Ge, Zhao, Yu and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

