A novel host restriction factor MRPS6 mediates the inhibition of PDCoV infection in HIEC-6 cells
- PMID: 38919620
- PMCID: PMC11196785
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1381026
A novel host restriction factor MRPS6 mediates the inhibition of PDCoV infection in HIEC-6 cells
Abstract
Introduction: Porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) is a zoonotic pathogen with a global distribution, capable of infecting both pigs and humans. To mitigate the risk of cross-species transmission and potential outbreaks, it is crucial to characterize novel antiviral genes, particularly those from human hosts.
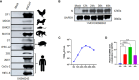
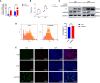
Methods: This research used HIEC-6 to investigate PDCoV infection. HIEC-6 cells were infected with PDCoV. Samples were collected 48 h postinfection for proteomic analysis.
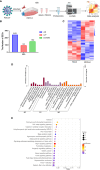
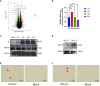
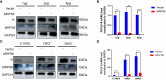
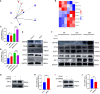
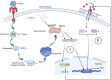
Results: We discovered differential expression of MRPS6 gene at 48 h postinfection with PDCoV in HIEC-6 cells. The gene expression initially increased but then decreased. To further explore the role of MRPS6 in PDCoV infection, we conducted experiments involving the overexpression and knockdown of this gene in HIEC-6 and Caco2 cells, respectively. Our findings revealed that overexpression of MRPS6 significantly inhibited PDCoV infection in HIEC-6 cells, while knockdown of MRPS6 in Caco2 cells led to a significant increase of virus titer. Furthermore, we investigated the correlation between PDCoV infection and the expression of MRPS6. Subsequent investigations demonstrated that MRPS6 exerted an augmentative effect on the production of IFN-β through interferon pathway activation, consequently impeding the progression of PDCoV infection in cellular systems. In conclusion, this study utilized proteomic analysis to investigate the differential protein expression in PDCoV-infected HIEC-6 cells, providing evidence for the first time that the MRPS6 gene plays a restrictive role in PDCoV virus infection.
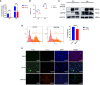
Discussion: Our findings initially provide the validation of MRPS6 as an upstream component of IFN-β pathway, in the promotion of IRF3, IRF7, STAT1, STAT2 and IFN-β production of HIEC-6 via dual-activation from interferon pathway.
Keywords: IFN-β; MRPS6; PDCoV; host restriction factor; proteomics.
Copyright © 2024 Jiang, Zhang, Li, Chen, Hao, Gao, Hao, Xu, Wang, Li and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of PDCoV-Infected HIEC-6 Cells and Enrichment Pathways PI3K-Akt and P38 MAPK.Viruses. 2024 Apr 9;16(4):579. doi: 10.3390/v16040579. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675921 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus nucleocapsid protein antagonizes JAK-STAT signaling pathway by targeting STAT1 through KPNA2 degradation.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0033424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00334-24. Epub 2024 Jun 3. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38829137 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) infection suppresses RIG-I-mediated interferon-β production.Virology. 2016 Aug;495:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.04.025. Epub 2016 May 3. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27152478 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, immune evasion mechanism and vaccine development of porcine Deltacoronavirus.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Apr 24;24(3):79. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01346-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38653845 Review.
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus and its prevalence in China: a review of epidemiology, evolution, and vaccine development.Arch Virol. 2021 Nov;166(11):2975-2988. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-05226-4. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Arch Virol. 2021. PMID: 34524535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, phylogenetics, and characterization of a new PDCoV strain that affects cellular gene expression in human cells.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1534907. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1534907. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40207165 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SNPs and Candidate Genes Associated with Monocyte/Lymphocyte Ratio and Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio in Duroc × Erhualian F2 Population.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 9;25(17):9745. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179745. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosco-Lauth AM, Hartwig AE, Porter SM, Gordy PW, Nehring M, Byas AD, et al. . Experimental infection of domestic dogs and cats with sars-cov-2: pathogenesis, transmission, and response to reexposure in cats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2020) 117:26382–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013102117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

