CCT and Cullin1 Regulate the TORC1 Pathway to Promote Dendritic Arborization in Health and Disease
- PMID: 38920658
- PMCID: PMC11201622
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13121029
CCT and Cullin1 Regulate the TORC1 Pathway to Promote Dendritic Arborization in Health and Disease
Abstract
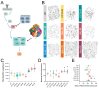
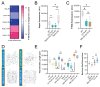
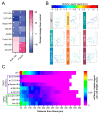
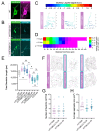
The development of cell-type-specific dendritic arbors is integral to the proper functioning of neurons within their circuit networks. In this study, we examine the regulatory relationship between the cytosolic chaperonin CCT, key insulin pathway genes, and an E3 ubiquitin ligase (Cullin1) in dendritic development. CCT loss of function (LOF) results in dendritic hypotrophy in Drosophila Class IV (CIV) multi-dendritic larval sensory neurons, and CCT has recently been shown to fold components of the TOR (Target of Rapamycin) complex 1 (TORC1) in vitro. Through targeted genetic manipulations, we confirm that an LOF of CCT and the TORC1 pathway reduces dendritic complexity, while overexpression of key TORC1 pathway genes increases the dendritic complexity in CIV neurons. Furthermore, both CCT and TORC1 LOF significantly reduce microtubule (MT) stability. CCT has been previously implicated in regulating proteinopathic aggregation, thus, we examine CIV dendritic development in disease conditions as well. The expression of mutant Huntingtin leads to dendritic hypotrophy in a repeat-length-dependent manner, which can be rescued by Cullin1 LOF. Together, our data suggest that Cullin1 and CCT influence dendritic arborization through the regulation of TORC1 in both health and disease.
Keywords: Drosophila; E3 ubiquitin ligase; Huntingtin; TORC1; chaperone; dendrite development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Update of
-
CCT and Cullin1 regulate the TORC1 pathway to promote dendritic arborization in health and disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 2:2023.07.31.551324. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.31.551324. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cells. 2024 Jun 13;13(12):1029. doi: 10.3390/cells13121029. PMID: 37577581 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Dewey E.H. The No-Breakfast Plan and the Fasting-Cure. 4th ed. The Health Culture Co.; New York, NY, USA: 1900.
-
- Miles W.R., Root H.F. Psychologic Tests Applied to Diabetic Patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1922;30:767–777. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1922.00110120086003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

