Survival after Stereotactic Radiosurgery in the Era of Targeted Therapy: Number of Metastases No Longer Matters
- PMID: 38920712
- PMCID: PMC11202506
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31060228
Survival after Stereotactic Radiosurgery in the Era of Targeted Therapy: Number of Metastases No Longer Matters
Abstract
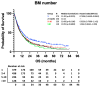
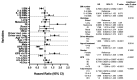
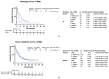
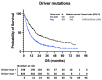
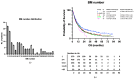
Randomised control trial data support the use of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in up to 4 brain metastases (BMs), with non-randomised prospective data complementing this for up to 10 BMs. There is debate in the neuro-oncology community as to the appropriateness of SRS in patients with >10 BMs. We present data from a large single-centre cohort, reporting survival in those with >10 BMs and in a >20 BMs subgroup. A total of 1181 patients receiving SRS for BMs were included. Data were collected prospectively from the time of SRS referral. Kaplan-Meier graphs and logrank tests were used to compare survival between groups. Multivariate analysis was performed using the Cox proportional hazards model to account for differences in group characteristics. Median survival with 1 BM (n = 379), 2-4 BMs (n = 438), 5-10 BMs (n = 236), and >10 BMs (n = 128) was 12.49, 10.22, 10.68, and 10.09 months, respectively. Using 2-4 BMs as the reference group, survival was not significantly different in those with >10 BMs in either our univariable (p = 0.6882) or multivariable analysis (p = 0.0564). In our subgroup analyses, median survival for those with >20 BMs was comparable to those with 2-4 BMs (10.09 vs. 10.22 months, p = 0.3558). This study contributes a large dataset to the existing literature on SRS for those with multi-metastases and supports growing evidence that those with >10 BMs should be considered for SRS.
Keywords: brain metastases; number of metastases; stereotactic radiosurgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tabouret E., Chinot O., Metellus P., Tallet A., Viens P., Gonçalves A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: An overview. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:4655–4662. - PubMed
-
- Reungwetwattana T., Nakagawa K., Cho B.C., Cobo M., Cho E.K., Bertolini A., Bohnet S., Zhou C., Lee K.H., Nogami N., et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:JCO2018783118. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.3118. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

