Do Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Have an Impact on Cognitive Decline-Latest Research Review
- PMID: 38921285
- PMCID: PMC11203898
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12121170
Do Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Have an Impact on Cognitive Decline-Latest Research Review
Abstract
Background: Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are chronic skin diseases that affect the mental health of patients. The relationship between AD and psoriasis and cognitive processes in patients remains unclear. The aim of the review was to answer the question of whether AD and psoriasis have an impact on cognitive decline in patients.
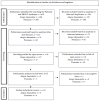
Method: A systematic literature search was conducted on PubMed and EBSCO to identify case-control, cross-sectional, or cohort studies that evaluated the association between atopic dermatitis and psoriasis and cognitive impairment.
Results: Most of the studies included in the review confirmed cognitive decline in patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Conclusions: It seems that atopic dermatitis and psoriasis may negatively affect cognitive processes such as working memory, concentration, attention, and speed of motor reactions. Psychological interventions targeting distorted cognitive processing could improve the quality of life of patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; cognitive impairment; cognitive processes; psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abrocitinib, tralokinumab and upadacitinib for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jan;28(4):1-113. doi: 10.3310/LEXB9006. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 38343072 Free PMC article.
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Educational and psychological interventions for managing atopic dermatitis (eczema).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 12;8(8):CD014932. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014932.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39132734 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Chiesa Fuxench Z.C., Block J.K., Boguniewicz M., Boyle J., Ong P.Y. Atopic Dermatitis in America Study: A Cross-Sectional Study Examining the Prevalence and Disease Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in the US Adult Population. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019;139:583–590. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.08.028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources