Impact of Nutrition Education on Various Health-Related Components of Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38921311
- PMCID: PMC11203892
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12121197
Impact of Nutrition Education on Various Health-Related Components of Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
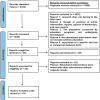
This study aimed to identify the impact of nutrition education on various health-related components of hemodialysis patients. A systematic review was conducted according to the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant literature published between 2013 and 2023 was identified across two databases (PubMed and Science Direct). The protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023460681). Two independent reviewers retrieved the data, and 41 studies were selected. Nine components related to the impact of nutrition education in hemodialysis patients were identified. Each component was clarified by mentioning each study and its results. This study enabled us to characterize the various components of the impact of nutritional education in hemodialysis patients, namely biological markers, quality of life, cost of care, adherence to dietary recommendations, knowledge, malnutrition inflammation, dietary intake, weight change, and behavior change. This systematic review enables healthcare providers to assess the impact of nutritional education on hemodialysis patients. Also, it gives professionals an exact idea of the impact of nutrition education on hemodialysis patients, with knowledge of new methods using behavior change theories and innovative technological tools.
Keywords: hemodialysis; nutrition education; review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Does exercise enhance the benefits of nutritional support on the biochemical markers of nutrition, anthropometry, and body composition in hemodialysis patients? A systematic review.Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 29;11:1471455. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1471455. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39677501 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of standardized nutrition guidelines by renal dietitians is associated with improved nutrition status.J Ren Nutr. 2009 Mar;19(2):136-44. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2008.11.002. J Ren Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19218040
-
Nutrition impact symptoms and associated outcomes in post-chemoradiotherapy head and neck cancer survivors: a systematic review.J Cancer Surviv. 2018 Aug;12(4):479-494. doi: 10.1007/s11764-018-0687-7. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Cancer Surviv. 2018. PMID: 29556926
Cited by
-
Association of dietary minerals and phosphorus to protein ratio with quality of life in Iranian Hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05637-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Non Communicable Diseases. [(accessed on 22 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases.
-
- Annual Data Report. [(accessed on 22 April 2024)]; USRDS. Available online: https://usrds-adr.niddk.nih.gov/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources