Comprehensive Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: How Nutrition, Dietary Polyphenols, Physical Activity, and Lifestyle Modifications Address Diabesity, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Neurodegenerative Conditions
- PMID: 38921462
- PMCID: PMC11206163
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo14060327
Comprehensive Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: How Nutrition, Dietary Polyphenols, Physical Activity, and Lifestyle Modifications Address Diabesity, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Neurodegenerative Conditions
Abstract
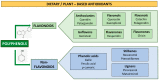
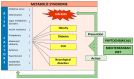
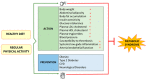
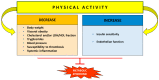
Several hallmarks of metabolic syndrome, such as dysregulation in the glucose and lipid metabolism, endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, low-to-medium systemic inflammation, and intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, represent a pathological bridge between metabolic syndrome and diabesity, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative disorders. This review aims to highlight some therapeutic strategies against metabolic syndrome involving integrative approaches to improve lifestyle and daily diet. The beneficial effects of foods containing antioxidant polyphenols, intestinal microbiota control, and physical activity were also considered. We comprehensively examined a large body of published articles involving basic, animal, and human studie, as well as recent guidelines. As a result, dietary polyphenols from natural plant-based antioxidants and adherence to the Mediterranean diet, along with physical exercise, are promising complementary therapies to delay or prevent the onset of metabolic syndrome and counteract diabesity and cardiovascular diseases, as well as to protect against neurodegenerative disorders and cognitive decline. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota reduces the risks associated with MS, improves diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and exerts neuroprotective action. Despite several studies, the estimation of dietary polyphenol intake is inconclusive and requires further evidence. Lifestyle interventions involving physical activity and reduced calorie intake can improve metabolic outcomes.
Keywords: diabesity; dietary polyphenols; metabolic syndrome; microbiota; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review from the Oxidative Stress to the Management of Related Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;12(12):2091. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122091. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Plant-Based Nutrition and Exercise in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 29;17(9):1498. doi: 10.3390/nu17091498. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabesity and Dietary Interventions: Evaluating the Impact of Mediterranean Diet and Other Types of Diets on Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Management.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 21;16(1):34. doi: 10.3390/nu16010034. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38201865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Targeting endothelial metaflammation to counteract diabesity cardiovascular risk: Current and perspective therapeutic options.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jun;120:226-241. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28408314 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting natural antioxidant polyphenols to protect neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 24;16:1492517. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1492517. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39981183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Diet on HDL in Obesity.Molecules. 2024 Dec 17;29(24):5955. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245955. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neurometabolic Function of the Dopamine-Aminotransferase System.Metabolites. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):21. doi: 10.3390/metabo15010021. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 39852364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing CNS Therapeutics: Enhancing Neurological Disorders with Nanoparticle-Based Gene and Enzyme Replacement Therapies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Feb 4;20:1443-1490. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S457393. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39925682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Composition of Ziziphus lotus (L.) Lam and Its Impact on the Metabolic Syndrome: A Review.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2025 Feb 17;2025:8276090. doi: 10.1155/adpp/8276090. eCollection 2025. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035065 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grundy S.M., Cleeman J.I., Daniels S.R., Donato K.A., Eckel R.H., Franklin B.A., Gordon D.J., Krauss R.M., Savage P.J., Smith S.C., Jr., et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005;112:2735–2752. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.105.169404. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

