Chemical-Saving Potential for Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Processes Based on Long-Term Pilot Trials
- PMID: 38921493
- PMCID: PMC11205864
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes14060126
Chemical-Saving Potential for Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Processes Based on Long-Term Pilot Trials
Abstract
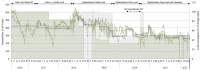
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have gained attraction in municipal wastewater treatment because of their capacity to meet strict water quality standards and support water reuse. Despite this, their operational sustainability is often compromised by high resource consumption, especially regarding the use of chemicals for membrane cleaning. This study explores innovative membrane-cleaning strategies to enhance the sustainability of MBR processes. Through long-term pilot trials at Stockholm's largest wastewater treatment plant, this study showed that alternative cleaning strategies can reduce chemical use by up to 75% without sacrificing treatment performance. The results further suggest that these alternative strategies could result in cost reductions of up to 70% and a reduction in environmental impacts by as much as 95% for certain indicators. Given that MBRs play a crucial role in addressing increasing treatment demands and advancing circular water management, the outcomes of this study are beneficial for the broader adoption of MBR processes. These results also have implications for existing installations, offering a pathway to more sustainable wastewater treatment. Moreover, the presented cleaning strategies provide significant opportunities for lowering operational costs and reducing the environmental footprint of new and existing MBR installations.
Keywords: cleaning chemicals; cost saving; environmental impact; membrane bioreactor; membrane cleaning; resource efficiency; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest. Sofia Andersson and Klara Westling were not employed by their current companies (Sweco Environment and Svenskt Vatten) when they contributed to the project. They started their positions after completing their parts of the project. The paper reflects the views of the scientists, not the companies.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Asheh S., Bagheri M., Aidan A. Membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: A review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021;4:100109. doi: 10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100109. - DOI
-
- The MBR Site. [(accessed on 2 February 2024)]. Available online: https://www.thembrsite.com/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources